Adenovirus Interstitial Nephritis After Kidney Transplant: Case Series and Literature Review
- PMID: 39982797
- PMCID: PMC12233852
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000000737
Adenovirus Interstitial Nephritis After Kidney Transplant: Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
Key Points:
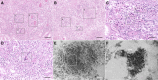
Adenovirus Interstitial Nephritis has nonspecific clinical manifestation, and kidney biopsy played an essential role in establishing its condition.
The most specific histopathological finding is interstitial nephritis with a granulomatous pattern.
The evolution is favorable in most cases, and there was recovery of kidney function a few months after the diagnostic.
Background: Post-kidney transplant (KT) adenovirus (AdV) nephritis is a condition with potential for acute allograft dysfunction, and evidence on its management is scarce.
Methods: This study is an original case series based on kidney biopsy (KB) of seven patients obtained at a health center specialized in kidney pathology from 2009 to 2023. We also performed a nonsystematic literature review on patients described in the literature.
Results: KB was used to define the diagnosis of all patients. The average time to diagnosis after transplantation was 32.9 months. The most prevalent symptoms were fever, macroscopic hematuria, and dysuria. The GFR reduced on average four times in relation to the baseline GFR. The main findings of KB were acute tubular necrosis (100%), necrotizing granulomatous interstitial nephritis (100%), and viral inclusions (100%). The therapies used were human Igs, antivirals, and reduction of immunosuppression. The clinical course was favorable in six of the seven patients. Our literature review found 44 patients with AdV interstitial nephritis, and the outcome was favorable in most reported patients.
Conclusions: AdV interstitial nephritis is a rare condition with important implications for KT recipients. KB plays a very important role in confirmation. This study fills gaps in the current literature on AdV interstitial nephritis and contributes to the understanding of this potential complication in the follow-up of KT recipients.
Keywords: acute allograft rejection; acute kidney failure; kidney biopsy; kidney transplantation; nephritis; transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure forms, as provided by each author, are available with the online version of the article at
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

