SUMO2/3 conjugation of TDP-43 protects against aggregation
- PMID: 39982984
- PMCID: PMC11844728
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq2475
SUMO2/3 conjugation of TDP-43 protects against aggregation
Abstract
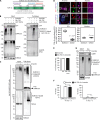
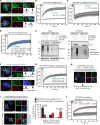
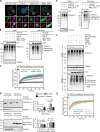
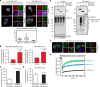
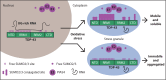
Cytosolic aggregation of the RNA binding protein TDP-43 (transactive response DNA-binding protein 43) is a hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Here, we report that during oxidative stress, TDP-43 becomes SUMO2/3-ylated by the SUMO E3 ligase protein PIAS4 (protein inhibitor of activated STAT 4) and enriches in cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs). Upon pharmacological inhibition of TDP-43 SUMO2/3-ylation or PIAS4 depletion, TDP-43 enrichment in SGs is accompanied by irreversible aggregation. In cells that are unable to assemble SGs, SUMO2/3-ylation of TDP-43 is strongly impaired, supporting the notion that SGs are compartments that promote TDP-43 SUMO2/3-ylation during oxidative stress. Binding of TDP-43 to UG-rich RNA antagonizes PIAS4-mediated SUMO2/3-ylation, while RNA dissociation promotes TDP-43 SUMO2/3-ylation. We conclude that SUMO2/3 protein conjugation is a cellular mechanism to stabilize cytosolic RNA-free TDP-43 against aggregation.
Figures




References
-
- Cook C. N., Wu Y., Odeh H. M., Gendron T. F., Jansen-West K., Del Rosso G., Yue M., Jiang P., Gomes E., Tong J., Daughrity L. M., Avendano N. M., Castanedes-Casey M., Shao W., Oskarsson B., Tomassy G. S., McCampbell A., Rigo F., Dickson D. W., Shorter J., Zhang Y. J., Petrucelli L., C9orf72 poly(GR) aggregation induces TDP-43 proteinopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eabb3774 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

