Rituximab for children with EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma in East Africa
- PMID: 39983056
- PMCID: PMC12141908
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024015234
Rituximab for children with EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma in East Africa
Abstract
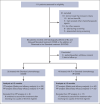
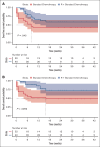
The addition of rituximab to the chemotherapy backbone was shown to significantly improve outcomes of children with aggressive high-grade lymphomas in high-income countries. However, data on its safety and efficacy in children with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive Burkitt lymphoma (BL) are limited. We conducted a prospective nonrandomized observational study in East African patients aged ≤25 years with confirmed BL. Patients received either the International Network for Cancer Treatment and Research (INCTR)-based standard chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and methotrexate [COM]) or rituximab plus standard chemotherapy (R-COM). The primary end point was safety. The secondary outcomes were event-free and overall survival and cost-effectiveness of incorporating rituximab. Primary analyses were conducted in the intention-to-treat population. The median follow-up was 23 months. Safety analyses included 72 patients: 32 in the COM group and 40 in the R-COM group. Grade ≥3 adverse events occurred in 18% of R-COM patients and 16% of COM patients. With respect to treatment outcomes at 12 months, 5 events were observed in the R-COM group and 14 in the COM group. The 12-month event-free survival was 67% with R-COM and 43% with COM (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24-0.98; P = .045). There were 8 deaths in the R-COM group, whereas 16 patients died in the COM group (HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.14-0.75; P = .009). R-COM was particularly effective in advanced-stage disease. The addition of rituximab to the INCTR-based protocol (COM) for EBV-positive BL has been observed to be safe and feasible in experienced centers in East Africa and saves lives.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.S. has received honoraria in the past 5 years from Oxford Nanopore Technology, Illumina, Exact Sciences, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Janssen; is a director and shareholder of SerenOx, an Oxford University social enterprise spin-off; and receives unrestricted research grants from AstraZeneca and Janssen. W.F.M. is a shareholder of SerenOx, and a director and a shareholder of SerenOx Africa Limited, a SerenOx partner company in Tanzania. C.C. is a director and shareholder of SerenOx Africa Limited. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

