Blebbisomes are large, organelle-rich extracellular vesicles with cell-like properties
- PMID: 39984653
- PMCID: PMC11906356
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-025-01621-0
Blebbisomes are large, organelle-rich extracellular vesicles with cell-like properties
Abstract
Cells secrete a large variety of extracellular vesicles (EVs) to engage in cell-to-cell and cell-to-environment intercellular communication. EVs are functionally involved in many physiological and pathological processes by interacting with cells that facilitate transfer of proteins, lipids and genetic information. However, our knowledge of EVs is incomplete. Here we show that cells actively release exceptionally large (up to 20 µm) membrane-enclosed vesicles that exhibit active blebbing behavior, and we, therefore, have termed them blebbisomes. Blebbisomes contain an array of cellular organelles that include functional mitochondria and multivesicular endosomes, yet lack a definable nucleus. We show that blebbisomes can both secrete and internalize exosomes and microvesicles. Blebbisomes are released from normal and cancer cells, can be observed by direct imaging of cancer cells in vivo and are present in normal bone marrow. We demonstrate that cancer-derived blebbisomes contain a plethora of inhibitory immune checkpoint proteins, including PD-L1, PD-L2, B7-H3, VISTA, PVR and HLA-E. These data identify a very large, organelle-containing functional EV that act as cell-autonomous mobile communication centres capable of integrating and responding to signals in the extracellular environment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






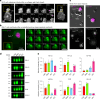









References
-
- Mathieu, M., Martin-Jaular, L., Lavieu, G. & Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol.21, 9–17 (2019). - PubMed
-
- van Niel, G. et al. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.23, 369–382 (2022). - PubMed
-
- van Niel, G., D’Angelo, G. & Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.19, 213–228 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DK111949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA274367/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 GM145399/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095811/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197570/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL159487/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- 1070985/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- 836090/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- R35GM125028/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- RM1GM145399/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 DK125546/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56AG068026/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- P50CA236733/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NCI | Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute (National Cancer Institute Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

