Pumilio differentially binds to mRNA 3' UTR isoforms to regulate localization of synaptic proteins
- PMID: 39984683
- PMCID: PMC11976915
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-025-00401-z
Pumilio differentially binds to mRNA 3' UTR isoforms to regulate localization of synaptic proteins
Abstract
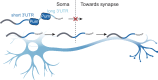
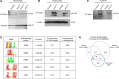
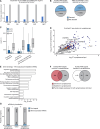
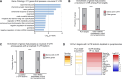
In neuronal cells, the regulation of RNA is crucial for the spatiotemporal control of gene expression, but how the correct localization, levels, and function of synaptic proteins are achieved is not well understood. In this study, we globally investigate the role of alternative 3' UTRs in regulating RNA localization in the synaptic regions of the Drosophila brain. We identify direct mRNA targets of the translational repressor Pumilio, finding that mRNAs bound by Pumilio encode proteins enriched in synaptosomes. Pumilio differentially binds to RNA isoforms of the same gene, favoring long, neuronal 3' UTRs. These longer 3' UTRs tend to remain in the neuronal soma, whereas shorter UTR isoforms localize to the synapse. In cultured pumilio mutant neurons, axon outgrowth defects are accompanied by mRNA isoform mislocalization, and proteins encoded by these Pumilio target mRNAs display excessive abundance at synaptic boutons. Our study identifies an important mechanism for the spatiotemporal regulation of protein function in neurons.
Keywords: Neuronal 3′ UTR; Pumilio; Synaptic Proteins; Synaptosome; mRNA Localization.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Andreassi C, Zimmermann C, Mitter R, Fusco S, De Vita S, Saiardi A, Riccio A (2010) An NGF-responsive element targets myo-inositol monophosphatase-1 mRNA to sympathetic neuron axons. Nat Neurosci 13:291–301 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

