Swallowing disorders in cerebral palsy: a systematic review of oropharyngeal Dysphagia, nutritional impact, and health risks
- PMID: 39985076
- PMCID: PMC11846443
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-025-01903-1
Swallowing disorders in cerebral palsy: a systematic review of oropharyngeal Dysphagia, nutritional impact, and health risks
Abstract
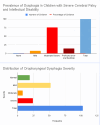
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a permanent disorder affecting movement and posture due to nonprogressive brain issues, often leading to various sensory, cognitive, and musculoskeletal challenges. Among these complications, oropharyngeal dysphagia (OPD) is prevalent, impacting up to 85% of children with CP and resulting in significant nutritional deficits. This systematic review aims to explore the prevalence and types of OPD in CP patients, its effects on nutritional status, and its associated health complications, emphasizing the need for thorough assessment and intervention to mitigate risks. The review adheres to PRISMA guidelines, searching five major databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Scopus) without time range restrictions to capture studies addressing swallowing disorders and their impact on nutritional status in CP. This review has been registered on Open OSF (n) 3KUQX. Individuals with CP often experience swallowing impairments, including delayed pharyngeal transit and aspiration. Research indicates that 81.5% of kids with CP suffer from dysphagia, commonly associated with reduced motor skills and general health. Moreover, as a result of these swallowing difficulties, nutritional complications may occur, with elevated levels of gastroesophageal symptoms causing malnutrition and growth delays, which require thorough evaluations and personalized interventions for successful treatment. Tools like the Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study were identified as primary methods for evaluation, but assessment remains limited by methodological inconsistencies. This systematic review underscores the significant health impacts of OPD in children with CP, which affects nutrition and overall well-being. Future research should address the need for standardized evaluation methods and effective interventions to balance nutritional needs with practical mealtime strategies.
Keywords: Cerebral Palsy; Health Complications; Neurorehabilitation; Nutritional Status; Oropharyngeal Dysphagia; Swallowing Disorders.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing of interests: The Authors declare no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Pham R, Mol BW, Gecz J, MacLennan AH, MacLennan SC, Corbett MA, Berry JG. Definition and diagnosis of cerebral palsy in genetic studies: a systematic review. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2020;62(9):1024–30. - PubMed
-
- Vitrikas K, Dalton H, Breish D. Cerebral palsy: an overview. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(4):213–20. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith S, McIntyre S, Blair E, Smithers-Sheedy H, Badawi N, Hansen M. Cerebral Palsy: Epidemiology. In: Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics: Genetic and Environmental Influences. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2023. p. 479–95.
-
- Arnaud C, Ehlinger V, Perraud A, Kinsner-Ovaskainen A, Klapouszczak D, Himmelmann K, Delobel-Ayoub M. Public health indicators for cerebral palsy: A European collaborative study of the Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe network. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology. 2023;37(5):404–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous