Synergistic effects of memantine and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PHA-543613 to improve memory of aged rats
- PMID: 39985181
- PMCID: PMC11929953
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaf014
Synergistic effects of memantine and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PHA-543613 to improve memory of aged rats
Abstract
Background: Combination treatments based on pharmacological interactions at α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are promising therapeutic approaches for neurocognitive disorders.
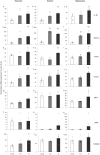
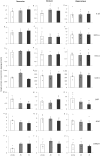
Methods: Here, we tested the cognitive efficacy of combinations of memantine with an α7 nAChR-selective agonist (PHA-543613) in naturally aged rats. Age-related changes in the expression of some key genes and proteins were also measured using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
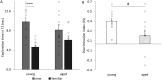
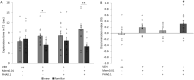
Results: Aged rats showed marked cognitive decline in the novel object recognition test, and they also exhibited cholinergic changes such as mRNA upregulation of α7 nAChRs. Upregulation of interleukin-1β, macrophage inflammatory protein 1α, CX3CL1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and ciliary neurotrophic factor mRNA was also detected in aged rats. Combination treatment of memantine and PHA-543613 successfully alleviated the age-related decline of recognition memory of rats by exceeding the effects of the corresponding monotreatments.
Conclusions: Results indicate a positive interaction between memantine and PHA-543613, which also reflects a putative role of α7 nAChRs in the cognitive enhancer effects of memantine. These findings may facilitate the development of combination therapies for age-related neurocognitive disorders.
Keywords: aging; alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; behavior; cytokine; neurocognitive disorder.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial, non-financial, or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cellular Mechanisms of Cognitive Enhancement: The In Vivo Modulation of the Firing Activity and the Responsiveness of Rat Hippocampal Neurons by Memantine and Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligands.ASN Neuro. 2024;16(1):2371160. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2024.2371160. Epub 2024 Jul 16. ASN Neuro. 2024. PMID: 39024573 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of cognitive enhancer effects of Alzheimer's disease medication memantine by alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PHA-543613 in the Morris water maze task.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Nov;238(11):3273-3281. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05942-4. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34387707 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoisomers of Chiral Methyl-Substituted Symmetric and Asymmetric Aryl Piperazinium Compounds Exhibit Distinct Selectivity for α9 and α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jul 16;16(14):2665-2681. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00204. Epub 2025 Jun 30. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40587620 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer's disease.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jan;10(1):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-160. doi: 10.3310/hta10010. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16409879
References
-
- Hou Y, Dan X, Babbar M, et al.Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:565–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Llaurador-Coll M, Rios S, García-Gavilán JF, et al.Plasma levels of neurology-related proteins are associated with cognitive performance in an older population with overweight/obesity and metabolic syndrome. GeroScience. 2023;45:2457–2470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-023-00764-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raina P, Santaguida P, Ismaila A, et al.Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:379–397. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-148-5-200803040-00009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsoi KKF, Chan JYC, Leung NWY, et al.Combination therapy showed limited superiority over monotherapy for Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis of 14 randomized trials. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17:863.e1–863.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.05.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balázs N, Bereczki D, Ajtay A, Oberfrank F, Kovács T.. Cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of dementia: real-life data in Hungary. GeroScience. 2022;44:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-021-00470-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UNKP-22-3 New National Excellence Program
- National Research, Development and Innovation Fund
- TKP2021-EGA-10/National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of the Hungarian Government
- TKP2021-EGA/National Research Development and Innovation Fund
- KA-2022-03/Medical School Research Foundation of the University of Pécs
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

