CpG-Based Nanovaccines Enhance Ovarian Cancer Immune Response by Gbp2-Mediated Remodeling of Tumor-Associated Macrophages
- PMID: 39985265
- PMCID: PMC12005807
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202412881
CpG-Based Nanovaccines Enhance Ovarian Cancer Immune Response by Gbp2-Mediated Remodeling of Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Abstract
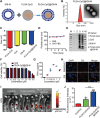
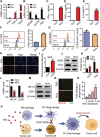
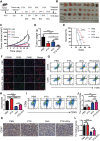
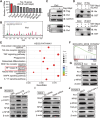
CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG), as an immunoadjuvant, can facilitate the transformation of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)into tumoricidal M1 macrophages. However, the accumulation of free CpG in tumor tissues remains a substantial challenge. To address this, a nanovaccine (PLGA-CpG@ID8-M) is engineered by encapsulating CpG within PLGA using ID8 ovarian cancer cell membranes (ID8-M). This nanovaccine demonstrates remarkable efficacy in reprogramming TAMs in ovarian cancer and significantly extends survival in ID8-bearing mice. Notably, these findings indicate that the nanovaccine can also mitigate chemotherapy-induced immunosuppression by increasing the proportion of M1-like TAMs and reducing the expression of CD47 on tumor cells, thereby achieving a synergistic effect in tumor immunotherapy. Mechanistically, through transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq), single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and mass spectrometry-based proteomics, it is elucidated that the nanovaccine enhances the expression of Gbp2 and promotes the recruitment of Pin1, which activates the NFκB signaling pathway, leading to the M1 polarization of TAMs. Furthermore, macrophages with elevated Gbp2 expression significantly inhibit tumor growth in both ID8 ovarian cancer and 4T1 breast cancer models. Conversely, targeting Gbp2 diminishes the antitumor efficacy of the nanovaccine in vivo. This study offers an innovative approach to immunotherapy and elucidates a novel mechanism (Gbp2-Pin1-NFκB pathway) for remodeling TAMs.
Keywords: Gbp2; TAMs; immunotherapy; nanovaccine; ovarian cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A dissolvable microneedle platform for the delivery of tumor-derived total RNA nanovaccines for enhanced tumor immunotherapy.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 1;199:120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.04.039. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40274056
-
A polymeric nanoplatform enhances the cGAS-STING pathway in macrophages to potentiate phagocytosis for cancer immunotherapy.J Control Release. 2024 Sep;373:447-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.07.039. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 39038546
-
Construction of pH-Sensitive Nanovaccines Encapsulating Tumor Cell Lysates and Immune Adjuvants for Breast Cancer Therapy.Small. 2023 Sep;19(37):e2301420. doi: 10.1002/smll.202301420. Epub 2023 May 8. Small. 2023. PMID: 37154213
-
CpG-Based Nanovaccines for Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug 5;16:5281-5299. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S317626. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34385817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Apr 23;30(4):26995. doi: 10.31083/FBL26995. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40302326 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2704100/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82001514/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82403482/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023BCA002/Major Science and Technology Foundation of Hubei Province
- 2023BAA016/Technology Research Project Foundation of Hubei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
