How I treat iron-refractory iron deficiency anaemia-An expert opinion-based treatment guidance for children and adults
- PMID: 39985323
- PMCID: PMC11985374
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.20030
How I treat iron-refractory iron deficiency anaemia-An expert opinion-based treatment guidance for children and adults
Abstract
Iron-refractory iron deficiency anaemia (IRIDA) is a rare hereditary microcytic anaemia characterized by partial or complete resistance to oral iron supplementation, caused by elevated plasma hepcidin levels resulting from pathogenic variants in the TMPRSS6 gene. Although intravenous iron supplementation is often effective, patient responses can vary significantly due to various factors, and potential side effects of this treatment remain unclear. Additionally, evidence-based international guidelines for diagnosing and managing IRIDA are lacking. This review aims to provide patient-tailored treatment strategies, informed by case studies and expert opinion, to address the specific therapeutic needs of both children and adults with IRIDA.
Keywords: hepcidin; iron distribution disorder; iron therapy; iron‐refractory iron deficiency anaemia.
© 2025 The Author(s). British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
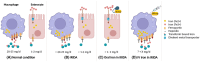

References
-
- Silvestri L, Nai A, Dulja A, Pagani A. Hepcidin and the BMP‐SMAD pathway: an unexpected liaison. Vitam Horm. 2019;110:71–99. - PubMed
-
- Finberg KE. Iron‐refractory iron deficiency anemia. Semin Hematol. 2009;46(4):378–386. - PubMed
-
- Donker AE, Galesloot TE, Laarakkers CM, Klaver SM, Bakkeren DL, Swinkels DW. Standardized serum hepcidin values in Dutch children: set point relative to body iron changes during childhood. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020;67(3):e28038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

