Human herpesvirus-associated transposable element activation in human aging brains with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39985481
- PMCID: PMC11846481
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14595
Human herpesvirus-associated transposable element activation in human aging brains with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
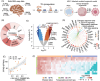
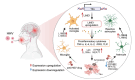
Introduction: Human herpesvirus (HHV) has been linked to Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the underlying mechanisms remain unknown.
Methods: We leveraged functional genomics data from Religious Orders Study or the Rush Memory and Aging Project (ROS/MAP) and Mount Sinai Brain Bank (MSBB) brain biobanks and single-cell RNA-sequencing data from HHV-infected forebrain organoids to investigate HHV-infection-associated transposable element (TE) dysregulation underlying AD etiologies.
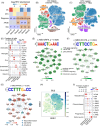
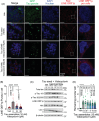
Results: We identified widespread TE dysregulation in HHV-positive human AD brains, including an astrocyte-specific upregulation of LINE1 subfamily TEs in HHV-positive human AD brains. We further pinpointed astrocyte-specific LINE1 upregulation that could potentially regulate target gene NEAT1 expression via long-range enhancer-promoter chromatin interactions. This LINE1 dysregulation can be partially reversed by the usage of anti-HHV drugs (valacyclovir and acyclovir) in a virus-infected human brain organoid model. Finally, we demonstrated that valacyclovir rescued tau-associated neuropathology and alleviated LINE1 activation in an experimental tau aggregation model.
Discussion: Our analysis provides associations linking molecular, clinical, and neuropathological AD features with HHV infection, which warrants future clinical validation.
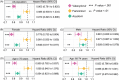
Highlights: Via analysis of bulk RNA-seq data in two large-scale human brain biobanks, ROS/MAP (n = 109 pathologically confirmed AD and n = 44 cognitively healthy controls) and MSBB (n = 284 AD and n = 150 cognitively healthy controls), we identified widespread TE activation in HHV-positive human AD brains and significantly positive associations of HHV RNA abundance with APOE4 genotype, Braak staging score, and CERAD score. We identified cell type-specific LINE1 upregulation in both microglia and astrocytes of human AD brains via long-range enhancer-promoter chromatin interactions on lncRNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1). We determined that usage of valacyclovir and acyclovir was significantly associated with reduced incidence of AD in a large real-world patient database. Using the HEK293 tau P301S model and U2OS mt-Keima cell model, we determined that valacyclovir treatment rescued tau-associated neuropathology and alleviated activation of LINE1 with increased cellular autophagy-level mechanistically supported clinical benefits of valacyclovir in real-world patient data.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease (AD); human herpesvirus (HHV); long interspersed nuclear element 2 (LINE1); neuroinflammation; transposable element (TE); valacyclovir.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C. (Dr. Cummings) has provided consultation to Acadia, Acumen, ALZpath, Annovis, Aprinoia, Artery, Biogen, Biohaven, BioXcel, Bristol‐Myers Squib, Eisai, Fosun, GAP Foundation, Green Valley, Janssen, Karuna, Kinoxis, Lighthouse, Lilly, Lundbeck, LSP/eqt, Mangrove Therapeutics, Merck, MoCA Cognition, New Amsterdam, Novo Nordisk, onocC4, Optoceutics, Otsuka, Oxford Brain Diagnostics, Praxis, Prothena, ReMYND, Roche, Scottish Brain Sciences, Signant Health, Simcere, sinaptica, T‐Neuro, TrueBinding, and Vaxxinity pharmaceutical, assessment, and investment companies. J.B.L. (Dr. Leverenz) has received consulting fees from Vaxxinity and grant support from GE Healthcare and serves on a data safety monitoring board for Eisai. E.F.F. (Dr. Fang) has a material transfer agreement (MTA) with LMITO Therapeutics Inc. (South Korea), a CRADA arrangement with ChromaDex (USA), and a commercialization agreement with Molecule AG/VITADAO and is a consultant to Aladdin Healthcare Technologies (UK and Germany), the Vancouver Dementia Prevention Centre (Canada), and Intellectual Labs (Norway). S.Q.C. has a commercialization agreement with Molecule AG/VITADAO. The other authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Itzhaki RF, Lin W‐Ru, Shang D, Wilcock GK, Faragher B, Jamieson GA. Herpes simplex virus type 1 in brain and risk of Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1997;349:241‐244. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R25 AG083721/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS133812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56AG074001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01AG066707-02S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG073323/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35AG071476/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 269901/Akershus University Hospital
- NINDS RO1NS139383/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01AG066707-01S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG065463/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG083003/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062428/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG076448/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 262960/Akershus University Hospital
- NIA R25AG083721-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 262175 334361/Research Council of Norway
- 282952/Cure Alzheimer's Fund
- R01 AG082118/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG083003/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG073323/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG074001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 AG071476/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 207819/Rosa sløyfe/Norwegian Cancer Society & Norwegian Breast Cancer Society
- RF1 AG082211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG082211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 282942/Molecule AG/VITADAO
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG082118/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1NS133812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG084250/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066707/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS139383/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG076448/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM109025/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 119986/NordForsk Foundation
- TO01000215/Czech Republic-Norway KAPPA programme
- P20 GM109025/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG066707/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 261973/Akershus University Hospital
- R01AG084250/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIA R35AG71476/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 281931/Civitan Norges Forskningsfond for Alzheimers sykdom
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

