Staphylococcal SplA and SplB serine proteases target ubiquitin(-like) specific proteases
- PMID: 39985644
- PMCID: PMC11846797
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-025-01841-5
Staphylococcal SplA and SplB serine proteases target ubiquitin(-like) specific proteases
Abstract
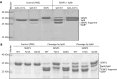
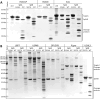
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive opportunistic pathogen that has colonized nearly 30% of the human population and can cause life-threatening infections. S. aureus exports a variety of virulence factors, such as a novel set of extracellular serine protease-like proteins (Spls). Spls are expressed by most clinical isolates of S. aureus, but their pathophysiological substrates and role during the infection are largely unknown. Here we characterized the substrate and cleavage specificity of recombinantly expressed SplA and SplB proteins. We identified a group of ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like modifying enzymes including deubiquitinating enzymes from human as well as from bacterial sources to be so far unknown SplA and SplB substrates. Distinct cleavage sites within these substrates for SplA (YLY↓T, FMY↓N) and SplB (VCD↓S) were identified by mass spectrometry and confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis of the target proteins. Since many cellular immune signaling pathways are tightly regulated by ubiquitination, the specific cleavage of ubiquitin modifying enzymes strongly suggests a specific role of Spls in manipulating immune signaling and in competing with other bacteria.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; Deubiquitination; Protein degradation; Serine protease-like; SplA; SplB.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Barnett TC, Liebl D, Seymour LM, Gillen CM, Lim JY, LaRock CN, Davies MR, Schulz BL, Nizet V, Teasdale RD, Walker MJ (2013) The globally disseminated M1T1 clone of group A Streptococcus evades autophagy for intracellular replication. Cell Host Microbe 14:675–682. 10.1016/j.chom.2013.11.003 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cox J, Mann M (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26:1367–1372. 10.1038/nbt.1511 - PubMed
-
- Dasari P, Nordengrün M, Vilhena C, Steil L, Abdurrahman G, Surmann K, Dhople V, Lahrberg J, Bachert C, Skerka C, Völker U, Bröker BM, Zipfel PF (2022) The protease SplB of Staphylococcus aureus targets host complement components and inhibits complement-mediated bacterial opsonophagocytosis. J Bacteriol 204:e0018421. 10.1128/JB.00184-21 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dubin G, Stec-Niemczyk J, Kisielewska M, Pustelny K, Popowicz GM, Bista M, Kantyka T, Boulware KT, Stennicke HR, Czarna A, Phopaisarn M, Daugherty PS, Thøgersen IB, Enghild JJ, Thornberry N, Dubin A, Potempa J (2008) Enzymatic activity of the Staphylococcus aureus SplB serine protease is induced by substrates containing the sequence Trp-Glu-Leu-Gln. J Mol Biol 379:343–356. 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.059 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

