Multiomic QTL mapping reveals phenotypic complexity of GWAS loci and prioritizes putative causal variants
- PMID: 39986281
- PMCID: PMC11960542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100775
Multiomic QTL mapping reveals phenotypic complexity of GWAS loci and prioritizes putative causal variants
Abstract
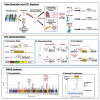
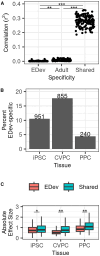
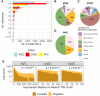
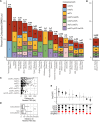
Most GWAS loci are presumed to affect gene regulation; however, only ∼43% colocalize with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs). To address this colocalization gap, we map eQTLs, chromatin accessibility QTLs (caQTLs), and histone acetylation QTLs (haQTLs) using molecular samples from three early developmental-like tissues. Through colocalization, we annotate 10.4% (n = 540) of GWAS loci in 15 traits by QTL phenotype, temporal specificity, and complexity. We show that integration of chromatin QTLs results in a 2.3-fold higher annotation rate of GWAS loci because they capture distal GWAS loci missed by eQTLs, and that 5.4% (n = 13) of GWAS colocalizing eQTLs are early developmental specific. Finally, we utilize the iPSCORE multiomic QTLs to prioritize putative causal variants overlapping transcription factor motifs to elucidate the potential genetic underpinnings of 296 GWAS-QTL colocalizations.
Keywords: GWAS; QTLs; chromatin accessibility QTLs; expression QTLs; histone acetylation QTLs; iPSC-derived cardiovascular progenitors; iPSC-derived pancreatic precursors; induced pluripotent stem cells; multiomic QTLs; quantitative trait loci.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.C.I.B. is the Founding Scientist and Director of the San Diego Institute of Science at Altos Labs.
Figures



Update of
-
Multi-omic QTL mapping in early developmental tissues reveals phenotypic and temporal complexity of regulatory variants underlying GWAS loci.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 11:2024.04.10.588874. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.10.588874. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Genom. 2025 Mar 12;5(3):100775. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100775. PMID: 38645112 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Nguyen J.P., Arthur T.D., Fujita K., Salgado B.M., Donovan M.K.R., iPSCORE Consortium. Matsui H., Kim J.H., D’Antonio-Chronowska A., D’Antonio M., Frazer K.A. eQTL mapping in fetal-like pancreatic progenitor cells reveals early developmental insights into diabetes risk. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:6928. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42560-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jerber J., Seaton D.D., Cuomo A.S.E., Kumasaka N., Haldane J., Steer J., Patel M., Pearce D., Andersson M., Bonder M.J., et al. Population-scale single-cell RNA-seq profiling across dopaminergic neuron differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2021;53:304–312. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00801-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

