Clinical and functional evidence for the pathogenicity of the LRRK2 p.Arg1067Gln variant
- PMID: 39988587
- PMCID: PMC11847920
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-00884-6
Clinical and functional evidence for the pathogenicity of the LRRK2 p.Arg1067Gln variant
Abstract
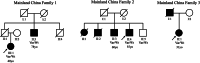
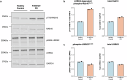
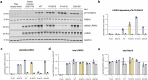
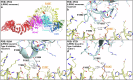
LRRK2-related Parkinson's disease (LRRK2-PD) is the most frequent form of monogenic PD worldwide, with important therapeutic opportunities, exemplified by the advancement in LRRK2 kinase inhibition studies/trials. However, many LRRK2 variants, especially those found in underrepresented populations, remain classified as variants of uncertain significance (VUS). Leveraging on Malaysian, Singaporean, and mainland Chinese PD datasets (n = 4901), we describe 12 Chinese-ancestry patients harboring the LRRK2 p.Arg1067Gln variant, more than doubling the number of previously reported cases (total n = 23, 87% East Asian, mean age of onset: 53.9 years). We determine that this variant is enriched in East Asian PD patients compared to population controls (OR = 8.0, 95% CI: 3.0-20.9), and provide supportive data for its co-segregation with PD, albeit with incomplete penetrance. Utilizing established experimental workflows, this variant showed increased LRRK2 kinase activity, by ~2-fold compared to wildtype and higher than the p.Gly2019Ser variant. Taken together, p.Arg1067Gln should be reclassified from a VUS to pathogenic for causing LRRK2-PD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Large-scale genetic characterization of Parkinson's disease in the African and African admixed populations.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 20:2025.01.14.25320205. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.14.25320205. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39867380 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Comprehensive LRRK2 and GBA screening in Portuguese patients with Parkinson's disease: identification of a new family with the LRRK2 p.Arg1441His mutation and novel missense variants.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013 Oct;19(10):897-900. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 28. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013. PMID: 23726462
-
LRRK2 Gly2019Ser penetrance in Arab-Berber patients from Tunisia: a case-control genetic study.Lancet Neurol. 2008 Jul;7(7):591-4. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70116-9. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Lancet Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18539535
-
LRRK2 low-penetrance mutations (Gly2019Ser) and risk alleles (Gly2385Arg)-linking familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease.Neurochem Res. 2007 Oct;32(10):1700-8. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9324-y. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17440812 Review.
-
Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase (LRRK2) Genetics and Parkinson's Disease.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;14:3-30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49969-7_1. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28353276 Review.
Cited by
-
The Global Landscape of Genetic Variation in Parkinson's disease: Multi-Ancestry Insights into Established Disease Genes and their Translational Relevance.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 11:2025.07.08.25330815. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.08.25330815. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672482 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Lim, S. Y. et al. Uncovering the genetic basis of Parkinson’s disease globally: from discoveries to the clinic. Lancet Neurol. 10.1016/s1474-4422(24)00378-8 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Mata, I. et al. LRRK2: Genetic mechanisms vs genetic subtypes. Handb. Clin. Neurol.193, 133–154, 10.1016/b978-0-323-85555-6.00018-7 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Alessi, D. R. & Sammler, E. LRRK2 kinase in Parkinson’s disease. Science360, 36–37, 10.1126/science.aar5683 (2018). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- MJFF-010188, MJFF-021041, MJFF-022659/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research (Michael J. Fox Foundation)
- MJFF-010188, MJFF-021041, MJFF-022659/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research (Michael J. Fox Foundation)
- MJFF-010188, MJFF-021041, MJFF-022659/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research (Michael J. Fox Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

