Harnessing ferroptosis for precision oncology: challenges and prospects
- PMID: 39988655
- PMCID: PMC11849278
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-025-02154-6
Harnessing ferroptosis for precision oncology: challenges and prospects
Abstract
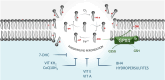
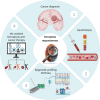
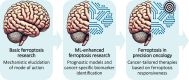
The discovery of diverse molecular mechanisms of regulated cell death has opened new avenues for cancer therapy. Ferroptosis, a unique form of cell death driven by iron-catalyzed peroxidation of membrane phospholipids, holds particular promise for targeting resistant cancer types. This review critically examines current literature on ferroptosis, focusing on its defining features and therapeutic potential. We discuss how molecular profiling of tumors and liquid biopsies can generate extensive multi-omics datasets, which can be leveraged through machine learning-based analytical approaches for patient stratification. Addressing these challenges is essential for advancing the clinical integration of ferroptosis-driven treatments in cancer care.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell-free DNA; DNA methylation; Ferroptosis; Liquid biopsy; Machine learning; Nanopore sequencing; Precision oncology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review of machine learning techniques for multi-omics data integration: challenges and applications in precision oncology.Brief Funct Genomics. 2024 Sep 27;23(5):549-560. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elae013. Brief Funct Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38600757 Review.
-
Realizing the promise of machine learning in precision oncology: expert perspectives on opportunities and challenges.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 17;25(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13621-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39962436 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing multimodal data integration to advance precision oncology.Nat Rev Cancer. 2022 Feb;22(2):114-126. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00408-3. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34663944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1361:249-268. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-91836-1_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35230693 Review.
-
Multimodal deep learning approaches for precision oncology: a comprehensive review.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae699. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae699. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39757116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying Fagopyrum dibotrys-derived nanovesicles induced ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a dual-pathway analysis of lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial damage.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1636149. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1636149. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40642010 Free PMC article.
-
Lipotoxicity, lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: a dilemma in cancer therapy.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Apr 26;41(1):75. doi: 10.1007/s10565-025-10025-7. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40285867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lockshin RA, Williams CM. Programmed cell death.2. Endocrine potentiation of the breakdown of the intersegmental muscles of silkmoths. J Insect Physiol. 1964;10(4):643–9. 10.1016/0022-1910(64)90034-4.
-
- Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER, Ackler SL, Catron ND, Chen J, et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):202–8. 10.1038/nm.3048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

