Combined effects of cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol alleviate migraine-like symptoms in mice
- PMID: 39988876
- PMCID: PMC12269478
- DOI: 10.1177/03331024251314487
Combined effects of cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol alleviate migraine-like symptoms in mice
Abstract
Background: The therapeutic use of cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) to treat migraine has been understudied. Using three mouse models, we examined the impact of CBD and THC on migraine-relevant behaviors triggered by: 1) calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), 2) sodium nitroprusside (SNP), and 3) cortical spreading depolarization (CSD).
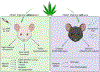
Methods: Both male and female CD1 mice were treated with CBD (100 mg/kg) or THC (1 mg/kg) alone or in combinations of CBD (1, 30 or 100 mg/kg) and THC (1 mg/kg) prior to injection of CGRP or SNP. The mice were assessed for light aversion (photophobia), squint (non-evoked pain), and periorbital tactile hypersensitivity, as well as possible adverse effects. In a separate set of experiments, CSD events were optogenetically induced in familial hemiplegic migraine 1 (FHM1) mutant and wildtype littermates (WT) mice (C57BL/6 background), followed by grimace and motor assessments with and without combinations of CBD (30 or 100 mg/kg) and THC (1 mg/kg).
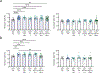
Results: In CD1 mice, a 100:1 CBD:THC combination mitigated light aversion induced by CGRP and SNP in males and females. Rescue of CGRP- and SNP-induced squint was observed only in male mice with 100:1 CBD:THC. None of the treatments rescued periorbital tactile hypersensitivity in either sex. In FHM1 mutant and WT mice, the 100:1 CBD:THC ratio did not affect CSD characteristics but did reduce CSD-induced grimace features (i.e., head pain mimic). No adverse effects of any of the cannabinoid treatments were observed using cognitive, emotional, or motor tests.
Conclusions: A 100:1 ratio of CBD:THC has a beneficial effect on some of the most bothersome migraine-related symptoms in three mouse models. Our findings support a potential therapeutic efficacy of combined CBD and THC treatments.
Keywords: CGRP; CSD; SNP; cannabinoids; headache; photophobia.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publicationof this article: AFR is a consultant and has stock in Delphian Therapeutics. He is also a consultant for Lundbeck, Abbvie, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Paragon, and holds patents on the CGRP monoclonal antibody for photophobia and diarrhea, on the PACAP monoclonal antibody for photophobia, and on the CGRP HO enhancer element. AMJMvdM and EAT received funding from Delphian Therapeutics and has been a consultant for Abbvie. Delphian Therapeutics is interested in the development of cannabis-derived migraine therapeutics and provided the commercially available cannabinoids used in the study in both labs. Delphian Therapeutics had no influence on the study design, data analysis, manuscript preparation or decision to publish, although the company was shown a preprint prior to submission. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The contents do not represent the views of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Figures







References
-
- Ashina M Migraine. N Engl J Med 2020; 383: 1866–1876. - PubMed
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018; 38: 1–211. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB and Ferrari MD. Migraine–current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 257–270. - PubMed
-
- Chandwani B, Bradley BA, Pace A, et al. The exploration of cannabis and cannabinoid therapies for migraine. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2023; 27: 339–350. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

