Physical activity may protect myelin via modulation of high-density lipoprotein
- PMID: 39989020
- PMCID: PMC11848041
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14599
Physical activity may protect myelin via modulation of high-density lipoprotein
Abstract
Introduction: Physical activity is associated with greater myelin content in older individuals with cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), a condition marked by demyelination. However, potential mechanisms underlying this relationship remain understudied.
Methods: We assessed cross-sectionally whether serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides moderated the association between physical activity and in vivo myelin in older individuals with CSVD and mild cognitive impairment.
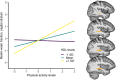
Results: We included 81 highly educated, community-dwelling older individuals (mean age 74.57 years), 64% of whom were female. Regression models revealed that HDL levels significantly moderated the relationship between physical activity and myelin in the sagittal stratum, wherein higher physical activity levels were linked to greater myelin levels for those with average or high HDL (standardized B [95% CI] = 0.289 [0.087 to 0.491], p = 0.006).
Discussion: Physical activity may promote myelin health partly through HDL. Data from longitudinal studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Highlights: Myelin loss is common in individuals with cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). Physical activity was positively associated with myelin in older adults with CSVD. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) levels were also positively related to myelin. Physical activity effects on myelin were moderated by HDL levels.
Keywords: aging; cerebrovascular health; exercise; fitness; lipids; neurodegeneration; white matter.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

