Parent Outcomes from a Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating a Modular Behavioral Intervention for Young Autistic Children
- PMID: 39989401
- PMCID: PMC11928905
- DOI: 10.1002/aur.70013
Parent Outcomes from a Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating a Modular Behavioral Intervention for Young Autistic Children
Abstract
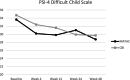
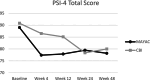
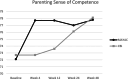
We assessed parent stress and competence outcomes from participation in a randomized controlled trial of a modular behavioral intervention (Modular Approach for Young Autistic Children; MAYAC) compared to a treatment-as-usual comprehensive behavioral intervention (CBI). Throughout their participation, parents of military families were included in their child's treatment (e.g., identifying goals, learning strategies to support their child) and reported on their feelings of stress using the Parenting Stress Index-4, Short Form (PSI-4), as well as their feelings of satisfaction and efficacy as a parent on the Parenting Sense of Competence (PSOC) scale. A linear mixed model evaluated the differences in stress and competence from baseline to each assessment period through follow-up. There were no significant differences between groups in stress or competence ratings; however, there were within-group changes in both treatment arms over the course of the trial. In both groups, parent stress decreased, and competence increased over time, continuing to suggest that behavioral analytic intervention for young children with autism can promote positive parent outcomes. Trial Registration: ClinicalTrial.gov identifier: NCT04078061.
Keywords: applied behavior analysis; autism; behavioral intervention; parent training; parental competence; parental stress; randomized clinical trial (RCT).
© 2025 The Author(s). Autism Research published by International Society for Autism Research and Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Some of the published materials to be used in the interventions have been developed by the investigators, for which they may receive royalties. This was disclosed to participants through informed consent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parent training interventions for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;2011(12):CD003018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003018.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 22161373 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness trial: Modular behavior approach for young autistic children compared to comprehensive behavioral intervention.Autism Res. 2024 Nov;17(11):2430-2446. doi: 10.1002/aur.3240. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Autism Res. 2024. PMID: 39375937 Clinical Trial.
-
Family-centred interventions for Indigenous early childhood well-being by primary healthcare services.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12(12):CD012463. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012463.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36511823 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness-enhanced parenting programmes for improving the psychosocial outcomes of children (0 to 18 years) and their parents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 10;1(1):CD012445. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012445.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38197473 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for parents of children and adolescents with chronic illness.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 15;4(4):CD009660. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009660.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 18;3:CD009660. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009660.pub4. PMID: 25874881 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Abidin, R. 1995. Manual for the Parenting Stress Index. Psychological Assessment Resources.
-
- Barroso, N. E. , Hungerford G. M., Garcia D., Graziano P. A., and Bagner D. M.. 2016. “Psychometric Properties of the Parenting Stress Index‐Short Form (PSI‐SF) in a High‐Risk Sample of Mothers and Their Infants.” Psychological Assessment 28, no. 10: 1331–1335. 10.1037/pas0000257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical