Exploring TGF-β Signaling in Cancer Progression: Prospects and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 39989503
- PMCID: PMC11846535
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S493643
Exploring TGF-β Signaling in Cancer Progression: Prospects and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
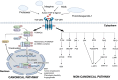
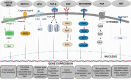
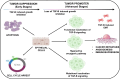
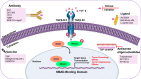
Cancer persists as a ubiquitous global challenge despite the remarkable advances. It is caused by uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis. The Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway is considered a primary regulator of various normal physiological processes in the human body. Recently, factors determining the nature of TGF-β response have received attention, specifically its signaling pathway which can be an attractive therapeutic target for various cancer treatments. The TGF-β receptor is activated by its ligands and undergoes transduction of signals via canonical (SMAD dependent) or non-canonical (SMAD independent) signaling pathways regulating several cellular functions. Furthermore, the cross talk of the TGF-β signaling pathway cross with other signaling pathways has shown the controlled regulation of cellular functions. This review highlights the cross talk between various major signaling pathways and TGF-β. These signaling pathways include Wnt, NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, and Hedgehog (Hh). TGF-β signaling pathway has a dual role at different stages. It can suppress tumor formation at early stages and promote progression at advanced stages. This complex behaviour of TGF-β has made it a promising target for therapeutic interventions. Moreover, many strategies have been designed to control TGF-β signaling pathways at different levels, inhibiting tumor-promoting while enhancing tumor-suppressive effects, each with unique molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. This review also discusses various therapeutic inhibitors including ligand traps, small molecule inhibitors (SMIs), monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), and antisense oligonucleotides which target specific components of TGF-β signaling pathway to inhibit TGF-β signaling and are studied in both preclinical and clinical trials for different types of cancer. The review also highlights the prospect of TGF-β signaling in normal physiology and in the case of dysregulation, TGF-β inhibitors, and different therapeutic effects in cancer therapy along with the perspective of combinational therapies to treat cancer.
Keywords: Hedgehog; cancer; canonical signaling pathway; combinational therapies; transforming growth factor beta; tumor promoting; tumor suppression.
© 2025 Sheikh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Rajput S, Sharma PK, Malviya R. Fluid mechanics in circulating tumour cells: role in metastasis and treatment strategies. Med Drug Discov. 2023;18:100158. doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2023.100158 - DOI
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(1):31–46. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

