Efficacy of ultrasonography and mammography in detecting features of breast cancer
- PMID: 39989587
- PMCID: PMC11844950
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1225_24
Efficacy of ultrasonography and mammography in detecting features of breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer (BC) is considered one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers. Early detection is critical for effective management. This study aims to assess the utility of ultrasonography (US) and mammography (MG) in detecting BC features.
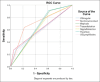
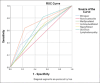
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional study involved the electronic records of 263 female patients diagnosed with BC. The mean age was 45.71 ± 12.25 years (17-90 years). A cross-tabulation test was performed to correlate the presence of each malignant feature (Yes/No) on both US and MG and the final ultrasonography diagnosis (benign/malignant). The compatibility between the presence of each feature on both imaging techniques was measured by the percentage of agreement in reporting the feature that was reported as Kappa. The sensitivity and specificity for each feature were calculated, and the receiver operating characteristic curve was used to measure the area under the curve for each feature on both modalities.
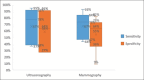
Results: The strong compatibility between the two techniques was 87.1%, 94.29%, 66.92%, 79.85%, 77.56%, 77.18, and 79.84% for irregular shape, uncircumscribed, spiculated margins, tissue distortion, nipple retraction, skin thickening, and the presence of lymphadenopathy, respectively (P < 0.001). Boxplots show that the sensitivity of the US ranged from 37% to 95%, and the specificity ranged from 27% to 91%. However, MG's sensitivity ranged from 44% to 93%, and the specificity ranged from 36% to 73%.
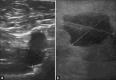
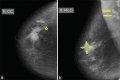
Conclusion: US and MG images show similar morphological changes, enhancing diagnostic accuracy in breast lesions. US characterizes echogenicity, provides real-time imaging, and uses color and pulsed Doppler techniques for vascularity and lymphadenopathy detection, while MG is better for identifying different calcification types.
Keywords: Breast cancer; irregular shape of breast lesion; mammography; spiculated margins of breast lesion; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of Ultrasound Imaging Features in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2023 Apr 17;15(4):e37691. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37691. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37206514 Free PMC article.
-
Primary neuroendocrine carcinomas of the breast and neuroendocrine differentiated breast cancers: Relationship between histopathological and radiological features.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Feb;147:110148. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110148. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35007984
-
Diagnostic Value of Elastography, Strain Ratio, and Elasticity to B-Mode Ratio and Color Doppler Ultrasonography in Breast Lesions.Int J Gen Med. 2020 May 25;13:215-224. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S247980. eCollection 2020. Int J Gen Med. 2020. PMID: 32547163 Free PMC article.
-
Breast lesions on chest computed tomography: pictorial review with mammography and ultrasound correlation.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015 Mar-Apr;44(2):144-54. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25442730 Review.
-
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Findings and Review of the Literature.Acad Radiol. 2023 Jun;30(6):1107-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Acad Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36357304 Review.
Cited by
-
The Rise and Refinement of Breast Thread Lifting: A Contemporary Review.J Clin Med. 2025 May 30;14(11):3863. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113863. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nafie MS, Boraei ATA. Exploration of novel VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors via design and synthesis of new alkylated indolyl-triazole Schiff bases for targeting breast cancer. Bioorg Chem. 2022;122:105708. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105708. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
