Molecular dynamics simulations reveal key roles of the LIF receptor in the assembly of human LIF signaling complex
- PMID: 39989618
- PMCID: PMC11847480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.01.014
Molecular dynamics simulations reveal key roles of the LIF receptor in the assembly of human LIF signaling complex
Abstract
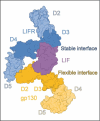
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) is a critical cytokine involved in various biological processes, including stem cell self-renewal, inflammation, and cancer progression. Structural studies have revealed how LIF forms a functional signaling complex. However, the dynamic binding pattern of the complex remains inadequately clarified. In this study, we employed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the recognition and binding mechanisms of LIF, revealing a preferential affinity for LIF Receptor (LIFR) over gp130, attributable to a larger buried surface area at the LIF-LIFR interface. Key residues F178 and K181 in FXXK motif, along with K124 in LIF helix B, mediate hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding and allosteric regulation, collectively stabilizing the LIF-LIFR interaction. We propose that the unique N-terminal extension of LIF enables signaling without requiring the additional receptor subunit beyond gp130 and LIFR, as verified by cell proliferation assays, distinguishing it from other cytokines in the LIF family. Additionally, analysis of domain fluctuations revealed that the LIF-LIFR interface undergoes less angular displacement compared to the LIF-gp130 interface, indicating a more stable interaction with LIFR. Together, these findings provide valuable insights into the molecular basis of LIF recognition and binding, offering a dynamic foundation for cytokine engineering.
Keywords: Gp130; LIF; LIFR; Molecular Dynamics.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
