Investigating the role of IDO1 in tumors: correlating IDO1 expression with clinical pathological features and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients
- PMID: 39989741
- PMCID: PMC11846502
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18776
Investigating the role of IDO1 in tumors: correlating IDO1 expression with clinical pathological features and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the role and expression patterns of IDO1 in various tumors, focusing on its correlation with clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients specifically diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods: Pan-cancer analysis assessed IDO1 function across different tumor types. Bioinformatics tools, immunohistochemistry techniques, and statistical analyses were employed to evaluate IDO1 expression levels and their association with clinical pathological features and prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
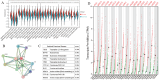
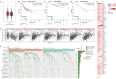
Results: IDO1 was found to be significantly overexpressed in various types of tumors, with higher levels correlating with poorer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). In lung adenocarcinoma patients, IDO1 protein was predominantly localized to the cytoplasm and cell membrane of tumor cells, with higher expression observed in tumor cells closer to normal lung tissue. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences in IDO1 expression based on the patient's clinical data, including gender, age, tumor location, allergy history, hypertension history, cardiovascular disease history, tumor history, diabetes (both type 1 and type 2), body mass index, smoking history, family history, alcohol history, and tumor maximum diameter (P > 0.05). However, IDO1 expression positively correlated with lymph node metastasis, pleural invasion, tumor recurrence, lower tumor differentiation, solid tumor components, preoperative chemotherapy, and clinical tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) staging (*P < 0.05), while negatively correlating with prior surgical history (*P < 0.05). Patients exhibiting high IDO1 expression levels demonstrated significantly worse PFS and OS (***P < 0.001 and **P = 0.003, respectively).
Conclusion: High IDO1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma correlates with increased tumor invasiveness, metastatic potential, advanced clinical stage, and poorer prognosis.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Expression; Function; IDO1; Lung adenocarcinoma; Prognosis.
©2025 Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bessede A, Peyraud F, Le Moulec S, Cousin S, Cabart M, Chomy F, Rey C, Lara O, Odin O, Nafia I, Guegan JP, Italiano A. Upregulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 in tumor cells and tertiary lymphoid structures is a hallmark of inflamed non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2023;29:4883–4893. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishnupuri KS, Alvarado DM, Khouri AN, Shabsovich M, Chen B, Dieckgraefe BK, Ciorba MA. IDO1 and kynurenine pathway metabolites activate PI3K-Akt signaling in the neoplastic colon epithelium to promote cancer cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. Cancer Research. 2019;79:1138–1150. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Della Corte CM, Ciaramella V, Ramkumar K, Vicidomini G, Fiorelli A, Nardone V, Cappabianca S, Cozzolino I, Zito Marino F, Di Guida G, Wang Q, Cardnell R, Gay CM, Ciardiello D, Martinelli E, Troiani T, Martini G, Napolitano S, Wang J, Byers LA, Ciardiello F, Morgillo F. Triple blockade of Ido-1, PD-L1 and MEK as a potential therapeutic strategy in NSCLC. Journal of Translational Medicine. 2022;20:541. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03730-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

