The impact of urolithiasis on urology services in a high-prevalence region: A multicenter study
- PMID: 39990065
- PMCID: PMC11840314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajur.2024.04.001
The impact of urolithiasis on urology services in a high-prevalence region: A multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of upper urinary tract (UUT) urolithiasis on urology services in a region with a high prevalence of the condition, and analyze the trends in endourological procedures for treating UUT urolithiasis and the cost of treatments in 11 hospitals over the last 6 years.
Methods: Using the hospital surgery statistics database, data were gathered from the urology departments of 11 hospitals in Saudi Arabia. The analysis focused on the trends, distribution, and annual cost of endourological procedures for UUT urolithiasis from January 2017 to December 2022.
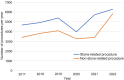
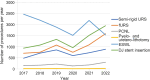
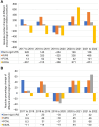
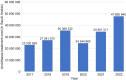
Results: Out of the total surgery performed (54 711), over half (31 039, 57%) were related to UUT urolithiasis. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) was the most performed procedure among stone-related procedures, accounting for 38% of all procedures. Double-J stent insertion, flexible ureteroscopy (URS), semi-rigid URS, percutaneous nephrolithotomy, and pyelo- and uretero-lithotomy accounted for 25%, 19%, 14%, 3.8%, and 0.35%, respectively. Notably, the number of stone-related UUT procedures in 2022 increased by 35% (from 4671 to 6283) compared to 2017. In the year 2022 compared to 2017, there was a statistically significant increase in the rate of all stone-related UUT procedures (p<0.001), except for ESWL and pyelo- and uretero-lithotomy. The rates of ESWL procedures reduced from 21% in 2017 to 13% in 2022 (p<0.001). Overall, the total cost of treatments has been estimated to be about 192.1 million SAR from 2017 to 2022 with an increase by 107% (47.7 million SAR in 2022 vs. 23.0 million SAR in 2017).
Conclusion: Our research findings suggest that urolithiasis poses a significant burden, accounting for over half of all urological surgery performed at the participating centers. Furthermore, there has been a 35% rise in stone-related UUT procedures over the past 6 years. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy, flexible URS, and semi-rigid URS have experienced significant increase in usage. Furthermore, in 2022 the cost of urolithiasis treatments has been more than doubled compared to 2017.
Keywords: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy; Percutaneous nephrolithotomy; Saudi Arabia; Ureteroscopy; Urinary stone.
© 2025 Editorial Office of Asian Journal of Urology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.Vé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Raheem O.A., Khandwala Y.S., Sur R.L., Ghani K.R., Denstedt J.D. Burden of urolithiasis: trends in prevalence, treatments, and costs. Eur Urol Focus. 2017;3:18–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

