Inhibition of GRK2-PDE4D Axis Suppresses Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Hyperplasia and Alleviates Experimental Arthritis
- PMID: 39990667
- PMCID: PMC11844291
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.100176
Inhibition of GRK2-PDE4D Axis Suppresses Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Hyperplasia and Alleviates Experimental Arthritis
Abstract
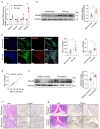
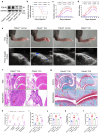
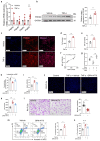
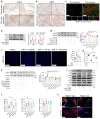
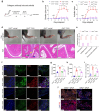
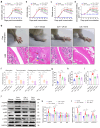
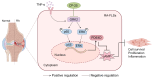
PDE4D has been reported to exhibit significantly elevated levels in the synovium of RA patients compared with OA, yet its role in RA remains underexplored. This study aimed to elucidate the role of the GRK2-PDE4D axis in FLSs and explore its potential as a therapeutic target for RA. Abundant expression of both PDE4D and GRK2 was observed in synovial tissues from both experimental arthritis animals and RA patients, with synchronized expression noted in RA patients. Global deletion of Pde4d reduced disease incidence and alleviated arthritis in CIA mice. TNF-α upregulated PDE4D expression, causing abnormal FLSs activation and hyperproliferation. Inhibiting PDE4D restored cAMP levels, thereby reducing FLSs hyperproliferation, migration, and anti-apoptosis. Mechanistically, TNF-α-induced PDE4D upregulation was dependent on GRK2. Inhibition of GRK2 with CP-25, an esterification modification of paeoniflorin, reduced PDE4D expression and FLSs proliferation, while restoring cAMP levels. Both genetic deficiency and pharmacological inhibition of GRK2 decreased PDE4D expression, ameliorating arthritis severity in animal models. This is the first study to investigate the role of PDE4D in RA and to clarify that it can be regulated by GRK2. These findings suggest that targeting the GRK2-PDE4D axis represents a promising therapeutic strategy for RA.
Keywords: CP-25; Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; G protein coupled receptor kinase 2; Phosphodiesterase 4D; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paeoniflorin-6'-O-benzene sulfonate down-regulates CXCR4-Gβγ-PI3K/AKT mediated migration in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting GRK2 translocation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 4;526(3):805-812. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.164. Epub 2020 Apr 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32268958
-
CP-25 reverses prostaglandin E4 receptor desensitization-induced fibroblast-like synoviocyte dysfunction via the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in autoimmune arthritis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Aug;40(8):1029-1039. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0196-2. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30643209 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α impairs EP4 signaling through the association of TRAF2-GRK2 in primary fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Feb;43(2):401-416. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00654-z. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 33859345 Free PMC article.
-
CP-25 inhibits the hyperactivation of rheumatic synoviocytes by suppressing the switch in Gαs-Gαi coupling to the β2-adrenergic receptor.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 30;21(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01358-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38037039 Free PMC article.
-
Role and mechanism of fibroblast-activated protein-α expression on the surface of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:1135384. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135384. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Van der Woude D, van der Helm-van Mil AHM. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and disease outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32:174–87. - PubMed
-
- He Y, Huang Y, Mai C, Pan H, Luo HB, Liu L. et al. The immunomodulatory role of PDEs inhibitors in immune cells: therapeutic implication in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res. 2020;161:105134. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Wei W, Zhang L, Xu HM. Effects and mechanisms of total glucosides of paeony on synoviocytes activities in rat collagen-induced arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;121:43–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

