Integrative Disulfidptosis-Based Risk Assessment for Prognostic Stratification and Immune Profiling in Glioma
- PMID: 39993959
- PMCID: PMC11850091
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70429
Integrative Disulfidptosis-Based Risk Assessment for Prognostic Stratification and Immune Profiling in Glioma
Abstract
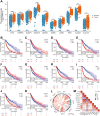
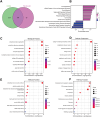
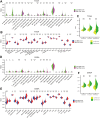
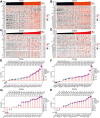
Disulfidptosis, a new form of programmed cell death, plays a role in multiple types of cancer. However, research on disulfidptosis in glioma is lacking. A disulfidptosis-associated risk score was constructed using Cox regression modelling, while LASSO regression was applied for feature selection. To explore the relationship between the risk score and the immune microenvironment, we employed CIBERSORT, ssGSEA and ESTIMATE algorithms. Additionally, wet lab experiments were conducted to validate the functional role of the key disulfidptosis gene RPN1, demonstrating its ability to promote glioma cell proliferation and migration. Disulfidptosis genes were significantly upregulated in gliomas, influencing clinical features and survival. The risk score effectively predicted OS and varied among clinical subgroups. High-risk scores correlated with tumour growth, invasion and immunosuppression. Patients with different risk scores showed distinct immune cell infiltration patterns. Most immune checkpoints and chemokines were positively associated with risk scores. Laboratory findings confirmed that RPN1 significantly promoted glioma cell proliferation and migration. Disulfidptosis-based risk assessment stratifies glioma prognosis and reveals immune microenvironment characteristics, offering insights for personalised treatment strategies.
Keywords: disulfidptosis; glioma; immune microenvironment; prognosis; risk score.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

