Exosome-like nanovesicles derived from kale juice enhance collagen production by downregulating Smad7 in human skin fibroblasts
- PMID: 39996007
- PMCID: PMC11847687
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1486572
Exosome-like nanovesicles derived from kale juice enhance collagen production by downregulating Smad7 in human skin fibroblasts
Abstract
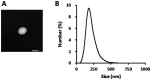
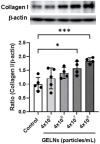
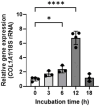
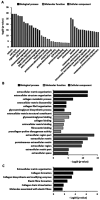
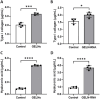
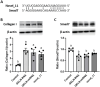
Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles (ELNs) are critical mediators of cross-kingdom communication, modulating gene expression in animal cells despite their plant origin. In this study, we investigated the effects of glucoraphanin-enriched kale (GEK)-derived ELNs (GELNs) on collagen production in normal human dermal fibroblasts NB1RGB. The ELNs isolated from GEK juice powder had particle sizes similar to those of typical exosomes. GELNs increased type I collagen expression in NB1RGB cells significantly. Microarray analysis demonstrated that GELN-derived total RNA upregulated the expression of genes related to extracellular matrix formation, including those involved in collagen synthesis. Further investigation revealed that microRNA-enriched fraction of GELNs promoted collagen production by inhibiting the expression of Smad7. These findings suggest that GELNs and their microRNA content enhance collagen production through the downregulation of Smad7.
Keywords: collagen; exosome-like nanovesicles; exosomes; fibroblasts; kale; miRNA.
Copyright © 2025 Hsu, Kamijyo, Koike, Ichikawa, Zheng, Ohno and Katayama.
Conflict of interest statement
TO was an employee of Yakult Health Foods Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

