A Silicon Rhodamine-fused Glibenclamide to Label and Detect Malaria-infected Red Blood Cells
- PMID: 39996370
- PMCID: PMC12002102
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202400628
A Silicon Rhodamine-fused Glibenclamide to Label and Detect Malaria-infected Red Blood Cells
Abstract
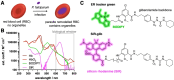
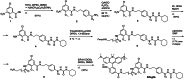
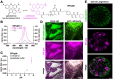
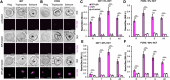
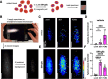
The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum affects the lives of millions of people worldwide every year. The detection of replicating parasites within human red blood cells is of paramount importance, requiring appropriate diagnostic tools. Herein, we design and apply a silicon rhodamine-fused glibenclamide (SiR-glib). We first test this far-red fluorescent, fluorogenic and endoplasmic reticulum-targeting sulfonylurea in mammalian cells and pancreatic islets, before characterizing its labeling performance in red blood cells infected with the asexual developmental stages of Plasmodium falciparum. We further combine SiR-glib with a portable smartphone-based microscope to easily and rapidly identify parasitized red blood cells, providing proof of principle for diagnostic use in rural endemic areas without major healthcare facilities.
Keywords: Malaria; Plasmodium falciparum; Red Blood Cells; Silicon Rhodamine; Smartphone-Based Detection.
© 2025 The Author(s). ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A. is an employee of Novo Nordisk A/S. D.J.H. and J.B. receives licensing revenue from Celtarys Research for provision of chemical probes. D.J.H. has filed patents related to type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes therapy, unrelated to the present study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 101042046/European Union's Horizon Europe Framework Programme
- MR/S025618/1/MRC
- EP/X026833/1/UKRI ERC Frontier Research Guarantee
- 23/0006627/"Steve Morgan Foundation Type 1 Diabetes Grand Challenge"
- 715884/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- NeuroNex2/ HA2686/19-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- 17/0005681/DUK_/Diabetes UK/United Kingdom
- 22/0006389/DUK_/Diabetes UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

