Association of Kidney Function With Incident Heart Failure: An Analysis of the Women's Health Initiative
- PMID: 39996449
- PMCID: PMC12132762
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037051
Association of Kidney Function With Incident Heart Failure: An Analysis of the Women's Health Initiative
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown an association of chronic kidney disease with heart failure (HF); however, this association has not been adequately examined in postmenopausal women, who are at heightened risk of both chronic kidney disease and HF. Additionally, association with HF subtypes is not well characterized.
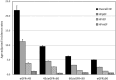
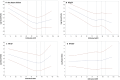
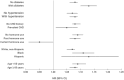
Methods and results: Incident HF was defined as first hospitalization for acute decompensated HF, obtained by self-reported outcomes followed by physician adjudication through review of hospital records. Chronic kidney disease was defined using estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Restricted cubic splines tested the association of eGFR with incident overall HF, and HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and preserved EF (HFpEF). Cox proportional hazards regression models evaluated the multivariable-adjusted association of eGFR categories with incident HF and its subtypes. The primary analysis included 23 309 women with 11 814 eGFR ≥90, 10 191 eGFR between 60 and 89, 1048 eGFR between 45 and 59 and 256 eGFR <45 mL/min per 1.73 m2. For overall HF, HFrEF and HFpEF, there was a stepwise increase in risk for incident HF with declining eGFR category. Associations were stronger for HFpEF (hazard ratio [HR], 2.80 [95% CI, 2.36-3.32]) than for HFrEF (HR, 2.18 [95% CI, 1.66-2.87]) for eGFR <45 as compared with eGFR ≥90. Heterogeneity of the HF subdistributions (HFpEF versus HFrEF) was significant (P=0.017).
Conclusions: Kidney dysfunction is associated with incident HF in postmenopausal women. Although lower eGFR is associated with both incident HFrEF and HFpEF, the association is stronger with HFpEF.
Registration: URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov; Unique Identifier: NCT00000611.
Keywords: HFpEF; chronic kidney disease; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Taufiq Salahuddin is supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant 5T32HL007828‐24. The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immune Cell Therapy: Promising Approach to Reduce Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Heart Failure.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Mar 4;14(5):e039871. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.039871. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39998354 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van de Wouw J, Broekhuizen M, Sorop O, Joles JA, Verhaar MC, Duncker DJ, Danser AHJ, Merkus D. Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a focus on microcirculatory factors and therapeutic targets. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1108. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

