The Role of Impulse Oscillometry in Detection of Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm)
- PMID: 39996619
- PMCID: PMC11851355
- DOI: 10.3390/arm93010002
The Role of Impulse Oscillometry in Detection of Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm)
Abstract
Background: Information is limited regarding the role of impulse oscillometry (IOS) for the detection of preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm). Therefore, we aimed to study the diagnostic ability of IOS in differentiating between PRISm and healthy subjects.
Methods: This retrospective data collection was done at the Lung Health Center, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand between July 2019 and April 2022. The potential diagnostic possibilities of difference in resistance at 5 Hz (R5) and resistance at 20 Hz (R20) (R5-R20) for PRISm detection were analyzed.
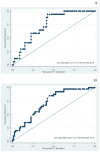
Results: The prevalence of PRISm was higher when using the fixed ratio (FR) criteria (FEV1/FVC ≥0.7 with FEV1 < 80% of predicted value) compared to the lower limit of normal (LLN) criteria (FEV1/FVC ≥ LLN and FEV1 < LLN) (10.0% vs. 4.2%). The %prediction for R5-R20 provided an acceptable area under the curve (AUC) for PRISm, defined by the LLN and the FR criteria (AuROC = 0.75 (95%CI; 0.64, 0.85) and 0.72 (95%CI; 0.63, 0.81), respectively). The cut-off value of %predicted R5-R20 ≥120% resulted in the highest sensitivity and specificity for detecting PRISm.
Conclusions: The %predicted of R5-R20 ≥ 120% showed an acceptable performance for PRISm detection and PRISm may be detected by IOS.
Keywords: impulse oscillometry; reactance; resistance; small airway disease; spirometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wan E.S., Castaldi P.J., Cho M.H., Hokanson J.E., Regan E.A., Make B.J., Beaty T.H., Han M.K., Curtis J.L., Curran-Everett D., et al. Epidemiology, genetics, and subtyping of preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) in COPDGene. Respir. Res. 2014;15:89. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0089-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wan E.S., Balte P., Schwartz J.E., Bhatt S.P., Cassano P.A., Couper D., Daviglus M.L., Dransfield M.T., Gharib S.A., Jacobs D.R., et al. Association Between Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry and Clinical Outcomes in US Adults. JAMA. 2021;326:2287–2298. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.20939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

