BCL-B Promotes Lung Cancer Invasiveness by Direct Inhibition of BOK
- PMID: 39996719
- PMCID: PMC11853756
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14040246
BCL-B Promotes Lung Cancer Invasiveness by Direct Inhibition of BOK
Abstract
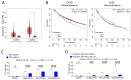
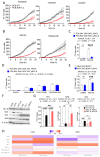
Expression of BCL-B, an anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family member, is correlated with worse survival in lung adenocarcinomas. Here, we show that BCL-B can mitigate cell death initiation through interaction with the effector protein BOK. We found that this interaction can promote sublethal mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and consequently generate apoptosis-flatliners, which represent a source of drug-tolerant persister cells (DTPs). The engagement of endothelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) further promotes cancer cell invasiveness in such DTPs. Our results reveal that BCL-B fosters cancer cell aggressiveness by counteracting complete MOMP.
Keywords: BCL-2 family; BCL-B; BOK; DTP; EMT; cancer; drug-resistance; invasiveness; mitochondrial permeabilization; persister phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 CA231620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DKH 70115382/German Cancer Aid (Max-Eder Junior Research Group Program, DKH 70115382)
- KA 4830/1-1/German Research Foundation (DFG, KA 4830/1-1)
- 01EO2104/Advanced Clinician Scientist Programm UMEA² (Medical Faculty, University Duisburg-Essen), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research 01EO2104 (BMBF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

