Blockade of the STAT3/BCL-xL Axis Leads to the Cytotoxic and Cisplatin-Sensitizing Effects of Fucoxanthin, a Marine-Derived Carotenoid, on Human Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 39997178
- PMCID: PMC11857094
- DOI: 10.3390/md23020054
Blockade of the STAT3/BCL-xL Axis Leads to the Cytotoxic and Cisplatin-Sensitizing Effects of Fucoxanthin, a Marine-Derived Carotenoid, on Human Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
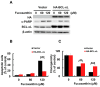
Bladder cancer is a globally prevalent urological malignancy, with transitional carcinoma (TCC) representing the majority of cases. Cisplatin is the primary drug for metastatic bladder cancer chemotherapy; however, its application is limited by nephrotoxicity and resistance. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) is an oncogenic transcription factor often overactivated in various cancers, making it an appealing drug target. Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid, has significant anticancer properties. This study explored Fucoxanthin's cytotoxic effects and its potential to potentiate the efficacy of Cisplatin, along with the mechanisms underlying these effects, on human bladder TCC cells. We demonstrated that Fucoxanthin is cytotoxic to bladder TCC cells by inducing apoptosis, evidenced by z-VAD-fmk-mediated annulment of Fucoxanthin's cytotoxicity. Furthermore, Fucoxanthin reduced the levels of inherent or interleukin-6-induced tyrosine 705-phosphorylated STAT3 accompanied by downregulating BCL-xL, a well-established STAT3 target. Notably, ectopic expression of STAT3-C, a dominant-active STAT3 mutant, or BCL-xL thwarted Fucoxanthin's proapoptotic and cytotoxic actions. Moreover, Fucoxanthin at subtoxic dosages enhanced the susceptibility to Cisplatin-induced apoptosis of bladder TCC cells initially resistant to Cisplatin. Remarkably, this Cisplatin-sensitizing effect of Fucoxanthin was abrogated when cells ectopically expressed STAT3-C or BCL-xL. Overall, for the first time, we proved that the proapoptotic, cytotoxic, and Cisplatin-sensitizing effects of Fucoxanthin on human bladder TCC cells are attributed to the blockade of the STAT3/BCL-xL axis. Our findings highlight that targeting the STAT3/BCL-xL axis is a promising strategy to eliminate bladder TCC cells and facilitate Cisplatin sensitization, and further support the potential of incorporating Fucoxanthin into Cisplatin-based chemotherapy for treating bladder cancer.
Keywords: BCL-xL; STAT3; apoptosis; bladder cancer; cisplatin; fucoxanthin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Fucoxanthin induces human melanoma cytotoxicity by thwarting the JAK2/STAT3/BCL-xL signaling axis.Environ Toxicol. 2024 Jun;39(6):3356-3366. doi: 10.1002/tox.24193. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Environ Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38444163
-
Sertindole, an Antipsychotic Drug, Curbs the STAT3/BCL-xL Axis to Elicit Human Bladder Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 24;24(14):11852. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411852. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511611 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptotanshinone Suppresses the STAT3/BCL-2 Pathway to Provoke Human Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Cell Death.Environ Toxicol. 2025 Apr;40(4):624-635. doi: 10.1002/tox.24446. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Environ Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39601353
-
Anticancer Effects of Fucoxanthin through Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis Induction, Angiogenesis Inhibition, and Autophagy Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 17;23(24):16091. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416091. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoxanthin: a marine carotenoid exerting anti-cancer effects by affecting multiple mechanisms.Mar Drugs. 2013 Dec 16;11(12):5130-47. doi: 10.3390/md11125130. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24351910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered exosomes: a promising design platform for overcoming cancer therapy resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Aug 6;13:1608480. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1608480. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40843170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

