Modern Smart Gadgets and Wearables for Diagnosis and Management of Stress, Wellness, and Anxiety: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39997286
- PMCID: PMC11855179
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13040411
Modern Smart Gadgets and Wearables for Diagnosis and Management of Stress, Wellness, and Anxiety: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
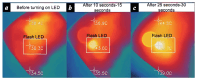
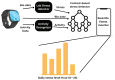
The increasing development of gadgets to evaluate stress, wellness, and anxiety has garnered significant attention in recent years. These technological advancements aim to expedite the identification and subsequent treatment of these prevalent conditions. This study endeavors to critically examine the latest smart gadgets and portable techniques utilized for diagnosing depression, stress, and emotional trauma while also exploring the underlying biochemical processes associated with their identification. Integrating various detectors within smartphones and smart bands enables continuous monitoring and recording of user activities. Given their widespread use, smartphones, smartwatches, and smart wristbands have become indispensable in our daily lives, prompting the exploration of their potential in stress detection and prevention. When individuals experience stress, their nervous system responds by releasing stress hormones, which can be easily identified and quantified by smartphones and smart bands. The study in this paper focused on the examination of anxiety and stress and consistently employed "heart rate variability" (HRV) characteristics for diagnostic purposes, with superior outcomes observed when HRV was combined with "electroencephalogram" (EEG) analysis. Recent research indicates that electrodermal activity (EDA) demonstrates remarkable precision in identifying anxiety. Comparisons with HRV, EDA, and breathing rate reveal that the mean heart rate employed by several commercial wearable products is less accurate in identifying anxiety and stress. This comprehensive review article provides an evidence-based evaluation of intelligent gadgets and wearable sensors, highlighting their potential to accurately assess stress, wellness, and anxiety. It also identifies areas for further research and development.
Keywords: anxiety; health sensors; psychological behavioral; smart gadgets; stress detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Panicker S.S., Gayathri P. A survey of machine learning techniques in physiology-based mental stress detection systems. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2019;39:444–469. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2019.01.004. - DOI
-
- Viveros J., Schramm D.G. Why Stress Management Strategies Work. Utah State University Extension; Orem, UT, USA: 2018.
-
- Kushlev K., Dunn E.W. Checking email less frequently reduces stress. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015;43:220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.005. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

