Comparison of Commercially Available Thermostable DNA Polymerases with Reverse Transcriptase Activity in Coupled Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays
- PMID: 39997635
- PMCID: PMC11858481
- DOI: 10.3390/mps8010011
Comparison of Commercially Available Thermostable DNA Polymerases with Reverse Transcriptase Activity in Coupled Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays
Abstract
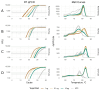
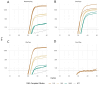
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is an important tool for the detection of target RNA molecules and the assay of RNA pathogens. Coupled RT-PCR is performed with an enzyme mixture containing a reverse transcriptase and a thermostable DNA polymerase. To date, several biotechnological companies offer artificial thermostable DNA polymerases with a built-in reverse transcriptase activity for use in the coupled RT-PCR instead of the enzyme mixtures. Here, we compared the artificial DNA polymerases and conventional enzyme mixtures for the RT-PCR by performing end-point and real-time RT-PCR assays using severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) RNA and endogenous mRNA molecules as templates. We found that the artificial enzymes were suitable for different RT-PCR applications, including SARS-CoV2 RNA detection but not for long-fragment RT-PCR amplification.
Keywords: GAPDH mRNA; SARS-CoV2; beta-2-microglobulin mRNA; reverse transcriptase; reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; thermostable DNA polymerase.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Konstantin A. Blagodatskikh was employed by the Center of Genetics and Reproductive Medicine “Genetico” PJSC. Author Dmitriy A. Varlamov was employed by the Syntol JSC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of an efficient one-step real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction method for severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 detection.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 4;16(6):e0252789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252789. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34086827 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric thermostable DNA polymerases with reverse transcriptase and attenuated 3'-5' exonuclease activity.Biochemistry. 2006 Oct 24;45(42):12786-95. doi: 10.1021/bi0609117. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 17042497
-
A comparative study on the efficiency of commercial reverse transcriptase-Polymerase chain reaction kits for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections.Indian J Public Health. 2022 Jul-Sep;66(3):276-281. doi: 10.4103/ijph.ijph_2042_21. Indian J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36149104
-
Amplification, detection, and automated sequencing of gibbon interleukin-2 mRNA by Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction.Anal Biochem. 1990 Nov 1;190(2):292-6. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90196-g. Anal Biochem. 1990. PMID: 2291473
-
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for prostate specific antigen in the management of prostate cancer.J Urol. 1997 Aug;158(2):326-37. J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9224297 Review.
References
-
- Varlamov D.A., Blagodatskikh K.A., Smirnova E.V., Kramarov V.M., Ignatov K.B. Combinations of PCR and Isothermal Amplification Techniques Are Suitable for Fast and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Viral RNA. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020;8:604793. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.604793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garafutdinov R.R., Mavzyutov A.R., Alekseev Y.I., Vorobev A.A., Nikonorov Y.M., Chubukova O.V., Matniyazov R.T., Baymiev A.K., Maksimov I.V., Kuluev B.R., et al. Human Betacoronaviruses and Their Highly Sensitive Detection by PCR and Other Amplification Methods. Biomics. 2020;12:121–179. doi: 10.31301/2221-6197.bmcs.2020-7. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

