Rademikibart Treatment for Moderate-to-Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma: A Phase 2B Randomized Trial
- PMID: 39998473
- PMCID: PMC12091008
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202409-1708OC
Rademikibart Treatment for Moderate-to-Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma: A Phase 2B Randomized Trial
Abstract
Rationale: Rademikibart (formerly CBP-201) is an IL-4Rα-targeting antibody.
Objectives: To evaluate rademikibart in adults with moderate-to-severe, persistent, uncontrolled asthma.
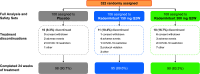
Methods: In this global phase 2b trial (NCT04773678), 322 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to two rademikibart groups (150 mg or 300 mg every other week, following a 600 mg loading dose) or placebo, administered subcutaneously, for 24 weeks.
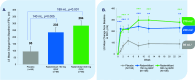
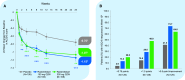
Measurements and main results: Prebronchodilator (trough) forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration (FEV1) at Week 12 (primary endpoint) improved with rademikibart 150 mg and 300 mg: least squares mean changes (95% CI), above placebo, were +140 mL (+44-236 mL; p=0.005) and +189 mL (+92-286 mL; p<0.001), respectively. Prebronchodilator trough FEV1 improvements occurred rapidly during Week 1, were sustained through Week 24, and greatest in patients with high baseline blood eosinophils (patients with ≥300 eosinophils/mL experienced placebo-adjusted FEV1 improvement at Week 24 of +420 mL [95% CI, +239-600 mL] in the 300 mg group). Rapid and sustained statistically significant improvements were also observed in percent predicted FEV1 and Asthma Control Questionnaire score across 24 weeks. Through Week 24, proportions of patients with ≥1 exacerbation were 7.5% (150 mg) and 9.3% (300 mg) vs 16.7% (placebo). 88% of patients completed treatment. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were generally similar to placebo, and no eosinophilia was observed. Injection site reactions were mostly mild. The most common TEAEs (10-12% of patients) were cough, COVID-19, and dyspnea.
Conclusions: Rapid and sustained improvements in lung function and asthma control were gained across 24 weeks of rademikibart therapy. This article is open access and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives License 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/). Clinical trial registration available at www.
Clinicaltrials: gov, ID: NCT04773678.
Keywords: CBP-201; IL-4Rα; asthma; rademikibart.
Figures


Comment in
References
-
- Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2023. Asthma data visualizations.https://www.cdc.gov/asthma/data-visualizations/default.htm
-
- Hankin CS, Bronstone A, Wang Z, Small MB, Buck P. Estimated prevalence and economic burden of severe, uncontrolled asthma in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2013;131(Suppl):AB126.
-
- Czira A, Turner M, Martin A, Hinds D, Birch H, Gardiner F, et al. A systematic literature review of burden of illness in adults with uncontrolled moderate/severe asthma. Respir Med . 2022;191:106670. - PubMed
-
- Nurmagambetov T, Kuwahara R, Garbe P. The economic burden of asthma in the United States, 2008–2013. Ann Am Thorac Soc . 2018;15:348–356. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

