Tau pathology is associated with postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) in early Alzheimer's disease in a sex-specific manner
- PMID: 39998900
- PMCID: PMC11853735
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70004
Tau pathology is associated with postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) in early Alzheimer's disease in a sex-specific manner
Abstract
Introduction: To investigate the associations of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) with tau deposition and cognitive ability in patients with early Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: Twenty-six cognitively impaired (CI) and 14 cognitively unimpaired (CU) individuals underwent mGluR5 positron emission tomography (PET) ([18F]PSS232), amyloid PET ([18F]florbetapir), and tau PET ([18F]MK6240), and neuropsychological assessment. The relationships among mGluR5 availability, tau deposition, and neuropsychological assessment were analyzed using Spearman's correlation and mediation analyses.
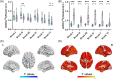
Results: CI patients had lower mGluR5 in the hippocampus than CU (standardized uptake value ratio [SUVr]: 2.03 ± 0.25 vs 1.79 ± 0.17, p = 0.003). Hippocampal mGluR5 was negatively associated with hippocampal tau deposition (r = -.46, p = 0.003) and positively associated with cognitive performance, but only in women. Hippocampal tau deposition mediated the effect of mGluR5 on cognitive performance.
Discussion: Reduced hippocampal mGluR5 is negatively related with tau deposition in most cortical regions and positively associated with cognitive performance, making it a promising biomarker for AD diagnosis and therapy.
Highlights: Cognitively impaired (CI) patients exhibited lower metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) availability in the hippocampus than cognitively unimpaired (CU) subjects. Hippocampal mGluR5 availability was negatively associated with tau deposition in widespread cortex. Hippocampal mGluR5 availability was positively associated with cognitive performance. The close association of mGluR5 with tau and cognition performance exists only in females. Tau pathology mediated the relationship between mGluR5 availability and cognition.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5); synapse; tau.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that they have no conflicts or competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Presynaptic density determined by SV2A PET is closely associated with postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 availability and independent of amyloid pathology in early cognitive impairment.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Jun;20(6):3876-3888. doi: 10.1002/alz.13817. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38634334 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) is associated with neurodegeneration and amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease: A [18F]PSS232 PET/MRI study.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jan 12;16(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01385-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38217040 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the relationship between synaptic density and metabotropic glutamate receptors in early Alzheimer's disease: a multi-tracer PET study.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 May 6;17(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01739-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40329311 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between flortaucipir PET tau binding and amyloid burden, clinical diagnosis, age and cognition.Brain. 2017 Mar 1;140(3):748-763. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww334. Brain. 2017. PMID: 28077397 Free PMC article.
-
Local and distant atrophy mediate the relationship between tau pathology and cognition in temporoparietal region in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Apr;104(4):1092-1102. doi: 10.1177/13872877251322539. Epub 2025 Mar 21. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40116643
Cited by
-
Spotlight on Alzheimer's disease and related dementias research in East Asia.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jul;21(7):e70479. doi: 10.1002/alz.70479. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40641055 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of longitudinal synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease using tau PET and plasma biomarkers.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 May;21(5):e70333. doi: 10.1002/alz.70333. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40432308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Migaud M, Charlesworth P, Dempster M, et al. Enhanced long‐term potentiation and impaired learning in mice with mutant postsynaptic density‐95 protein. Nature. 1998;396(6710):433‐439. - PubMed
-
- Davies CA, Mann DMA, Sumpter PQ, Yates PO. A quantitative morphometric analysis of the neuronal and synaptic content of the frontal and temporal cortex in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1987;78(2):151‐164. - PubMed
-
- Daggett LP, Sacaan AI, Akong M, et al. Molecular and functional characterization of recombinant human metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34(8):871‐886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

