Soluble RAGE enhances muscle regeneration after cryoinjury in aged and diseased mice
- PMID: 39999114
- PMCID: PMC11856280
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318754
Soluble RAGE enhances muscle regeneration after cryoinjury in aged and diseased mice
Abstract
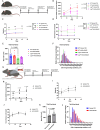
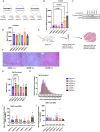
The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE), classically considered a mediator of acute and chronic inflammatory responses, has recently been implicated by genetic knockout studies as a regulator of skeletal muscle physiology during development and following acute injury. Yet, the role of its soluble isoform, soluble RAGE (sRAGE), in muscle regeneration remains relatively unexplored. To address this knowledge gap, Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) mediated and genetic knockin supplementation strategies were developed to specifically assess the effects of changing levels of sRAGE on muscle regeneration. We evaluated general muscle physiology and histology, including central nucleation, and myofiber size. We found that acute induction of sRAGE in aged and atherosclerotic animals accelerates muscle repair after cryoinjury. Similarly, genetic modification of the endogenous Ager gene locus to favor production of sRAGE over transmembrane RAGE accelerates repair of cryo-damaged skeletal muscle. However, increasing sRAGE via AAV delivery or using our transgenic mouse lines had no impact on muscle repair in aged or diseased mice after barium chloride (BaCl2) injury. Together, these studies identify a unique muscle regulatory activity of sRAGE that is variable across injury models and may be targeted in a context-specific manner to alter the skeletal muscle microenvironment and boost muscle regenerative output.
Copyright: © 2025 Horwitz et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
A.J.W. is a scientific advisor for Kate Therapeutics and Frequency Therapeutics, as well as a co-founder and scientific advisory board member and holds private equity in Elevian, Inc., a company that aims to develop medicines to restore regenerative capacity. Elevian also has provided sponsored research to the Wagers lab.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

