Activating the d-Tagatose Production Capacity of Escherichia coli with Structural Insights into C4 Epimerase Specificity
- PMID: 39999377
- PMCID: PMC11907403
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c12842
Activating the d-Tagatose Production Capacity of Escherichia coli with Structural Insights into C4 Epimerase Specificity
Abstract
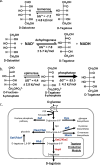
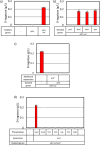
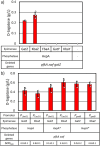
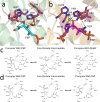
d-Tagatose, a rare low-calorie sweetener, is ideal for beverages due to its high solubility and low viscosity. Current enzymatic production methods from d-galactose or d-galactitol are limited by reaction reversibility, affecting the yield and purity. This study demonstrates that Escherichia coli harbors a thermodynamically favorable pathway for producing d-tagatose from d-glucose via phosphorylation-epimerization-dephosphorylation steps. GatZ and KbaZ, annotated as aldolase chaperones, exhibit C4 epimerization activity, converting d-fructose-6-phosphate to d-tagatose-6-phosphate. Structural analysis reveals active site differences between these enzymes and class II aldolases, indicating functional divergence. By exploiting the strains' inability to metabolize d-tagatose, carbon starvation was applied to remove sugar byproducts. The engineered strains converted 45 g L-1 d-glucose to d-tagatose, achieving a titer of 7.3 g L-1 and a productivity of 0.1 g L-1 h-1 under test tube conditions. This approach highlights E. coli as a promising host for efficient d-tagatose production.
Keywords: d-tagatose; metabolic engineering; rare sugars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The authors declare the following financial interests which may be considered as potential competing interests: Dileep Sai Kumar Palur, Jayce E. Taylor, Bryant Luu, Augustine Arredondo, Ian C. Anderson, Trevor Gannalo, Justin B. Siegel, and Shota Atsumi are inventors on the patent application related to this study. John Didzbalis is employed by Mars, Incorporated, a manufacturer of food and confectionery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characteristics of a fructose 6-phosphate 4-epimerase from Caldilinea aerophila DSM 14535 and its application for biosynthesis of tagatose.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020 Sep;139:109594. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109594. Epub 2020 May 17. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020. PMID: 32732042
-
Protein Engineering of Tagatose 4-Epimerase for D-Tagatose Production.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 May 21;73(20):12353-12363. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c01663. Epub 2025 May 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40350604
-
TM0416, a Hyperthermophilic Promiscuous Nonphosphorylated Sugar Isomerase, Catalyzes Various C5 and C6 Epimerization Reactions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 May 1;83(10):e03291-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03291-16. Print 2017 May 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28258150 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on Biological Production of a Functional Low-Calorie Sugar d-Tagatose.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Jul 30;73(30):18511-18524. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c04610. Epub 2025 Jul 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40690603 Review.
-
The use of isomerases and epimerases for the production of the functional sugars mannose, allulose and tagatose from Fructose.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 9;41(4):129. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04344-4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40202705 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Phosphatase Reverses the Leloir Pathway to Promote Tagatose Synthesis from Glucose.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 1:2025.07.29.665981. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.29.665981. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766469 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Sugar Substitutes Market Size, Share, Forecast [Latest]. MarketsandMarkets, https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/sugar-substitute-market.... (accessed 21 Novermber 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

