Effect of β-casein A2 cow milk supplementation on physical growth, inflammation, growth-related hormones, and nutritional biomarkers in stunted children
- PMID: 39999830
- PMCID: PMC12235434
- DOI: 10.6065/apem.2448158.079
Effect of β-casein A2 cow milk supplementation on physical growth, inflammation, growth-related hormones, and nutritional biomarkers in stunted children
Abstract
Purpose: Previous studies have suggested that milk consumption can promote growth in children. However, limited studies have been performed on the effects of cow milk varieties, especially β-casein A2 milk. This study aims to investigate the effect of β-casein A2 cow milk supplementation on physical growth, inflammation, and growth-related hormone and nutritional biomarker profiles in growth-stunted children.
Methods: This is a quasi-experimental study with only one group and a pre-and posttest design. This research is divided into 3 stages: allele testing in the β-casein gene, processing into ready-to-drink milk, and a clinical trial. The participants were children aged 12-36 months who were given 200-mL β-casein A2 cow milk supplementation once a day for 3 months. The outcome assessments were physical growth (body weight and height), inflammation (tumor necrosis factor-alpha [TNF-α] and cortisol levels), and biological markers related to growth and nutrition (insulin-like growth factor-1 [IGF-1], growth hormone [GH], and transferrin) that were measured during pre-, mid (week 6)-, and post (week 12)-intervention periods.
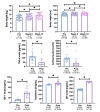
Results: This study included 30 study participants. Significant body weight and height improvements were observed at week 6 and postintervention (week 12) compared to preintervention. There were significant reductions in the inflammation markers TNF-α and cortisol levels postintervention. Additionally, IGF-1 and GH levels increased significantly, and transferrin levels also rose, potentially reflecting improved nutritional status.
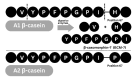
Conclusion: This study suggests that β-casein A2 milk supplementation was associated with improvements in physical growth and related biomarkers in stunted children. Additionally, β-casein A2 milk may produce fewer BCM-7 metabolites compared to β-casein A1 milk, which has been hypothesized to be associated with certain adverse health outcomes. However, further controlled studies are needed to confirm its efficacy as a dietary intervention.
Keywords: Caseins; Growth; Growth regulation; Hormones; Inflammation; Milk; Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF). UNICEF nutrition strategy 2020–2030: nutrition, for every child [Internet]. New York: UNICEF; 2024 [cited 2024 Jun 12]. Available from https://knowledge.unicef.org/childnutrition-and-development/resource/uni....
-
- World Health Organization. Joint child malnutrition estimates [Internet]. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2014 [cited 2024 Jun 12]. Available from https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/jointchild-malnutrition-....
-
- Data and Information Center of Ministry of Health of The Republic of Indonesia. Situation of Stunted Toddler in Indonesia [Internet]. Jakarta (Indonesia): Ministry of Health of The Republic of Indonesia; 2018 [cited 2024 Jun 12]. Available from https://independen.id/upload/DATA/Laporan%20Situasi%20Balita%20Pendek%20....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

