Unraveling ADHD: genes, co-occurring traits, and developmental dynamics
- PMID: 40000109
- PMCID: PMC11861640
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202403029
Unraveling ADHD: genes, co-occurring traits, and developmental dynamics
Abstract
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental condition with a high prevalence of co-occurring conditions, contributing to increased difficulty in long-term management. Genome-wide association studies have identified variants shared between ADHD and co-occurring psychiatric disorders; however, the genetic mechanisms are not fully understood. We integrated gene expression and spatial organization data into a two-sample Mendelian randomization study for putatively causal ADHD genes in fetal and adult cortical tissues. We identified four genes putatively causal for ADHD in cortical tissues (fetal: ST3GAL3, PTPRF, PIDD1; adult: ST3GAL3, TIE1). Protein-protein interaction databases seeded with the causal ADHD genes identified biological pathways linking these genes with conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) and biomarkers (e.g., lymphocyte counts) known to be associated with ADHD, but without previously shown genetic relationships. The analysis was repeated on adult liver tissue, where putatively causal ADHD gene ST3GAL3 was linked to cholesterol traits. This analysis provides insight into the tissue-dependent temporal relationships between ADHD, co-occurring traits, and biomarkers. Importantly, it delivers evidence for the genetic interplay between co-occurring conditions, both previously studied and unstudied, with ADHD.
© 2025 Miller et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

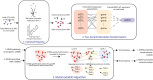





References
-
- Bunin A, Sisirak V, Ghosh HS, Grajkowska LT, Hou ZE, Miron M, Yang C, Ceribelli M, Uetani N, Chaperot L, et al. (2015) Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRS is an inhibitory receptor on human and murine plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Immunity 43: 277–288. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Hartman CA, Haavik J, Harro J, Klungsøyr K, Hegvik T-A, Wanders R, Ottosen C, Dalsgaard S, Faraone SV, et al. (2018) Common psychiatric and metabolic comorbidity of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One 13: e0204516. 10.1371/journal.pone.0204516 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
