[Experimental study on injection completion rate and performance for needle-free insulin injection]
- PMID: 40000191
- PMCID: PMC11955342
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202406035
[Experimental study on injection completion rate and performance for needle-free insulin injection]
Abstract
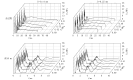
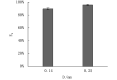
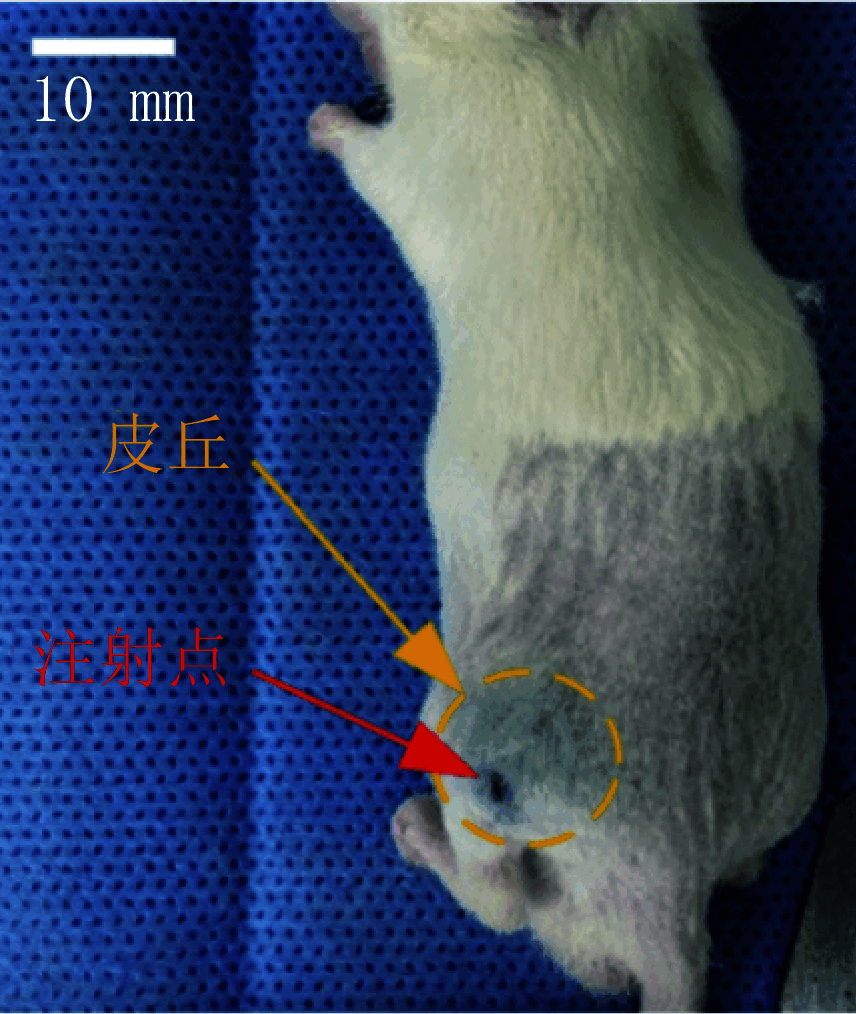
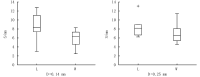
As a relatively novel technique for drug delivery, the needle-free injection technique is characterized by transporting the drug liquid to the designated subcutaneous position through a high-speed micro-jet. Although this technique has been applied in many fields, the research on its drug dispersion mechanism and injection performance is insufficient. The presented study aims to identify critical parameters during the injection process and describe their influence on the injection effect. The injection completion rate and performance of a needle-free injector under various operating conditions were compared based on mouse experiments. The results show that the nozzle diameter imposes a more significant influence on jet characteristics than other injection parameters. Moreover, the injection completion rate increases with the nozzle diameter. The nozzle diameters of 0.14 mm and 0.25 mm correspond to injection completion rates of 89.7% and 95.8%, respectively. Furthermore, by analyzing the rate of blood glucose change in the tested mice, it is found that insulin administration through the needle-free injection can achieve a drug effect duration longer than 120 min, which is better than that obtained using conventional needle-syringe technique. In summary, the obtained conclusions can provide an important reference for the optimal design and extending application of the air-powered needle-free injector.
无针注射技术是一种利用高速微射流将药液递送进皮下指定部位的新型给药手段。尽管目前无针注射技术已在多个领域得到应用,但针对其药液扩散机制和注射性能的研究仍存在一定的不足。本研究旨在确定无针注射过程中的关键参数,并描述其对注射效果的影响。本文通过小鼠实验的方法,比较了不同注射条件下无针注射器的注射完成率和注射性能。结果表明,相比于其它注射参数,喷嘴直径对射流性能的影响更为明显。此外,注射完成率随喷嘴直径增大而增加,当喷嘴直径为0.14 mm和0.25 mm时,注射完成率分别为89.7%和95.8%。进而,通过对小鼠血糖变化率的分析发现,采用无针注射的方式进行胰岛素给药可以获得超过120 min的药效持续时间,优于传统针头注射方式。综上,本文所得结论可为气动无针注射器的优化设计和拓展应用提供重要参考依据。.
Keywords: Injection completion rate; Insulin; Mouse; Needle-free injector; Skin mound.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:本文全体作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamic behavior of a spring-powered micronozzle needle-free injector.Int J Pharm. 2015 Aug 1;491(1-2):91-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.05.067. Epub 2015 May 29. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26027490
-
Drug injection and dispersion characteristics of an air-powered needle-free injector.Med Eng Phys. 2022 Nov;109:103906. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103906. Epub 2022 Oct 15. Med Eng Phys. 2022. PMID: 36371083
-
Experimental analysis of the performance of an air-powered needle-free liquid jet injector.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:3499-502. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610296. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013. PMID: 24110483
-
Jet injectors: Perspectives for small volume delivery with lasers.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Mar;182:114109. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114109. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 34998902 Review.
-
[Needle-free injection--science fiction or comeback of an almost forgotten drug delivery system?].Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2007 Aug;30(8):297-303. Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17879809 Review. German.
References
-
- Weniger B G, Papania M J Alternative vaccine delivery methods. Vaccines. 2013;61:1200–1231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
