Structural basis for lipid-mediated activation of G protein-coupled receptor GPR55
- PMID: 40000629
- PMCID: PMC11861906
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57204-y
Structural basis for lipid-mediated activation of G protein-coupled receptor GPR55
Abstract
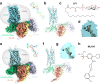
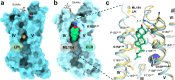
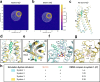
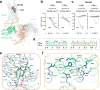
GPR55 is an orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) and represents a promising drug target for cancer, inflammation, and metabolic diseases. The endogenous activation of lipid GPCRs can be solely mediated by membrane components and different lipids have been proposed as endogenous activators of GPR55, such as cannabinoids and lysophosphatidylinositols. Here, we determine high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of the activated GPR55 in complex with heterotrimeric G13 and two structurally diverse ligands: the putative endogenous agonist 1-palmitoyl-2-lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) and the synthetic agonist ML184. These results reveal insights into ligand recognition at GPR55, G protein coupling and receptor activation. Notably, an orthosteric binding site opening towards the membrane is observed in both structures, enabling direct interaction of the agonists with membrane lipids. The structural observations are supported by mutagenesis and functional experiments employing G protein dissociation assays. These findings will be of importance for the structure-based development of drugs targeting GPR55.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Crucial Amino Acid Residues Involved in Agonist Signaling at the GPR55 Receptor.Biochemistry. 2017 Jan 24;56(3):473-486. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01013. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28005346 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical responsiveness of the orphan receptor GPR55 to cannabinoid ligands.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 23;284(43):29817-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.050187. Epub 2009 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19723626 Free PMC article.
-
GPR55, a lysophosphatidylinositol receptor with cannabinoid sensitivity?Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10(8):799-813. doi: 10.2174/156802610791164229. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20370712 Review.
-
Lysophosphatidylinositol causes neurite retraction via GPR55, G13 and RhoA in PC12 cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024284. Epub 2011 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21904624 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidylinositols, from Cell Membrane Constituents to GPR55 Ligands.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jun;39(6):586-604. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.02.011. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29588059 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of SC targeting RhoA regulation and its potential value in gastric cancer therapy.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jul 24;43:102158. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102158. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40746849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee, A. G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr.1666, 62–87 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Mizuno, H. & Kihara, Y. Druggable lipid signaling pathways. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1274, 223–258 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Smith, N. J. & Murray, F. Shifting our perspective on orphan G protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.31, 582–583 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

