Phytochemical profiling, antioxidant potential, and UHPLC-HRMS analysis of Phlomis genus aerial parts for therapeutic applications
- PMID: 40000650
- PMCID: PMC11861611
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-89055-4
Phytochemical profiling, antioxidant potential, and UHPLC-HRMS analysis of Phlomis genus aerial parts for therapeutic applications
Abstract
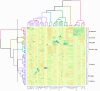
In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the therapeutic potential of Phlomis species, prompting numerous scientific studies on their pharmacological properties. However, the specific therapeutic applications of Phlomis remain underexplored, warranting further investigation. Iran, as one of the primary centers of diversity for the Phlomis genus in Asia, is home to 20 species, 9 of which are endemic to the region. This study aimed to conduct a comprehensive investigation and comparison of aerial part extracts from 56 Phlomis samples across 6 distinct Iranian species, focusing on their unique phenolic composition, antioxidant properties, and therapeutic potential. The analysis included a detailed assessment of total phenolics, flavonoids, tannin, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity, photosynthetic pigments, and ascorbic acid levels, along with measurements of their antioxidant activity. UHPLC-HRMS was also employed to identify unique chemical fingerprints. To interpret the extensive dataset, multivariate data analysis was applied, revealing correlations and distinctions among the different Phlomis species. Results showed that each species contains distinct polyphenols with known bioactivities, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antimicrobial, cardiovascular, and neuroprotective properties, suggesting the potential for targeted therapeutic applications of specific Phlomis species. In addition, the study found that variations in polyphenol profiles and antioxidant capabilities among Phlomis species are primarily driven by genetic factors rather than environmental conditions, highlighting the critical role of species selection in advancing plant-derived nutraceutical research and applications.
Keywords: Phlomis; Antioxidants; HCA and PCA; Polyphenolic compounds; UHPLC-HRMS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Guideline statement: Authors confirm that the use of plants in the present study complies with international, national and/or institutional guidelines.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chemometrics-based analysis of the phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity of Salvia species from Iran.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 27;14(1):17317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68421-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39068233 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of native wild Salvia nemorosa populations for chemical compositions, antioxidant activity and UHPLC-HRMS profiling.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83756-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738427 Free PMC article.
-
LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS characterization of phenolic compounds from Pyracantha coccinea M.Roem. and their antioxidant capacity.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2021 Jan 31;67(1):201-211. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2021.67.1.29. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2021. PMID: 34817347
-
Phlomis genus: bridging tradition and science in medicinal Research-a review of phytochemistry and pharmacological properties.Nat Prod Res. 2025 Jun;39(11):3281-3294. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2024.2423029. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 39616620 Review.
-
Exploring nutritional and bioactive properties of Maranta arundinacea L.: An unconventional food plant.Food Res Int. 2025 Jul;212:116462. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116462. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40382045 Review.
References
-
- Kurman, Y. & Pasin, O. Anticancer activity of endemic Phlomis extracts in HCT116 human Colon cancer cells. Sağlık Bilimlerinde Değer. 13, 227–233 (2023).
-
- Guven, L., Erturk, A., Koca, M. & Gulcin, I. Phenolic compounds of Phlomis tuberosa by LC–MS/MS-Determination of antioxidant activity, Molecular Docking, and enzyme inhibition profiles. Chem. Select8 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

