A feature explainability-based deep learning technique for diabetic foot ulcer identification
- PMID: 40000748
- PMCID: PMC11862115
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90780-z
A feature explainability-based deep learning technique for diabetic foot ulcer identification
Abstract
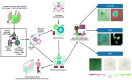
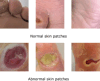
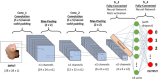
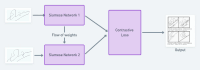
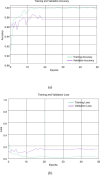
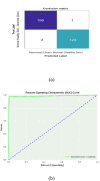
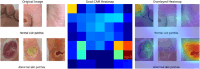
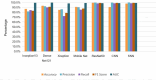
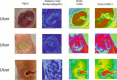
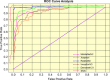
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a common and serious complication of diabetes, presenting as open sores or wounds on the sole. They result from impaired blood circulation and neuropathy associated with diabetes, increasing the risk of severe infections and even amputations if untreated. Early detection, effective wound care, and diabetes management are crucial to prevent and treat DFUs. Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly through deep learning, has revolutionized DFU diagnosis and treatment. This work introduces the DFU_XAI framework to enhance the interpretability of deep learning models for DFU labeling and localization, ensuring clinical relevance. The framework evaluates six advanced models-Xception, DenseNet121, ResNet50, InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, and Siamese Neural Network (SNN)-using interpretability techniques like SHAP, LIME, and Grad-CAM. Among these, the SNN model excelled with 98.76% accuracy, 99.3% precision, 97.7% recall, 98.5% F1-score, and 98.6% AUC. Grad-CAM heat maps effectively identified ulcer locations, aiding clinicians with precise and visually interpretable insights. The DFU_XAI framework integrates explainability into AI-driven healthcare, enhancing trust and usability in clinical settings. This approach addresses challenges of transparency in AI for DFU management, offering reliable and efficient solutions to this critical healthcare issue. Traditional DFU methods are labor-intensive and costly, highlighting the transformative potential of AI-driven systems.
Keywords: AI; DL; Diabetic Foot Ulcer; Heat Map; LIME.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Rufino, J. et al. Feature Selection for an Explainability Analysis in Detection of COVID-19 Active Cases from Facebook User-Based Online Surveys. medRxiv 2023-05. (2023).
-
- Gouverneur, P. J. Machine Learning Methods for Pain Investigation Using Physiological Signals. 6 (Logos Verlag Berlin GmbH, 2024).
-
- Ahsan, M. et al. A deep learning approach for diabetic foot ulcer classification and recognition. Information 14(1), 36. (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

