Neuronal polyunsaturated fatty acids are protective in ALS/FTD
- PMID: 40000803
- PMCID: PMC11976277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01889-3
Neuronal polyunsaturated fatty acids are protective in ALS/FTD
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Neuronal polyunsaturated fatty acids are protective in ALS/FTD.Nat Neurosci. 2025 Apr;28(4):913. doi: 10.1038/s41593-025-01926-1. Nat Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40055545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
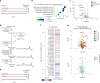
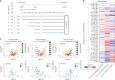
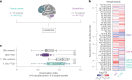
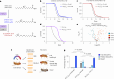
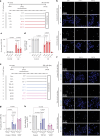
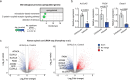
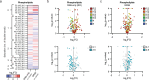
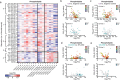
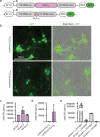
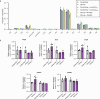
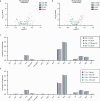
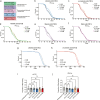
Here we report a conserved transcriptomic signature of reduced fatty acid and lipid metabolism gene expression in a Drosophila model of C9orf72 repeat expansion, the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD), and in human postmortem ALS spinal cord. We performed lipidomics on C9 ALS/FTD Drosophila, induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell neurons and postmortem FTD brain tissue. This revealed a common and specific reduction in phospholipid species containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Feeding C9 ALS/FTD flies PUFAs yielded a modest increase in survival. However, increasing PUFA levels specifically in neurons of C9 ALS/FTD flies, by overexpressing fatty acid desaturase enzymes, led to a substantial extension of lifespan. Neuronal overexpression of fatty acid desaturases also suppressed stressor-induced neuronal death in iPS cell neurons of patients with both C9 and TDP-43 ALS/FTD. These data implicate neuronal fatty acid saturation in the pathogenesis of ALS/FTD and suggest that interventions to increase neuronal PUFA levels may be beneficial.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mori, K. et al. The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat is translated into aggregating dipeptide-repeat proteins in FTLD/ALS. Science339, 1335–1338 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 NS123242/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS132836/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS123242/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- NS132836/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R00 NS123242/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

