Roles of mediodorsal thalamus in observational fear-related neural activity in mouse anterior cingulate cortex
- PMID: 40001162
- PMCID: PMC11853286
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-025-01188-9
Roles of mediodorsal thalamus in observational fear-related neural activity in mouse anterior cingulate cortex
Abstract
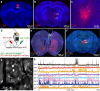
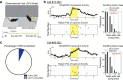
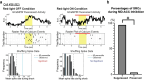
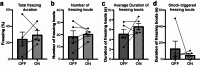
Observational fear (OF) is the ability to vicariously experience and learn from another's fearful situation, enabling adaptive responses crucial for survival. It has been shown that the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) are crucial for OF. A subset of neurons in the ACC is activated when observing aversive events in the demonstrator, which elicits OF. However, the neural circuit mechanisms underlying the expression of OF-related activity in the ACC remain unexplored. Previous studies have shown that the mediodorsal thalamus (MD) is crucial for OF, and MD neurons project to the ACC. Therefore, we hypothesize that the projection from MD to ACC may facilitate the OF-related activity in the ACC. By utilizing in vivo calcium imaging combined with the optogenetic terminal inhibition of MD-ACC pathway, we found that a subset of ACC neurons was activated when observing demonstrator's fearful situation in male mice. Furthermore, the optogenetic inhibition of the MD-ACC projection during the demonstrator's aversive moments significantly suppressed the OF-related activity in the ACC. Our data suggests that the MD-ACC projection plays a role in OF-related activity in ACC neurons.
Keywords: Anterior cingulate cortex; Calcium imaging; Empathy; Mediodorsal thalamus; Observational fear; Optogenetic inhibition.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All protocols regarding mouse use and treatment aligned with NIH guidelines, and procedures were approved by UT Southwestern Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anterior cingulate cortex and its input to the basolateral amygdala control innate fear response.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 16;9(1):2744. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05090-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30013065 Free PMC article.
-
Corticoamygdala Transfer of Socially Derived Information Gates Observational Learning.Cell. 2018 May 31;173(6):1329-1342.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 May 3. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29731170 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical representations of affective pain shape empathic fear in male mice.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 24;16(1):1937. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57230-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39994222 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Others' Distress Through Past Experiences: The Role of Memory Engram Cells in Observational Fear.Adv Neurobiol. 2024;38:215-234. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62983-9_12. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39008018 Review.
-
Short-term synaptic plasticity in the nociceptive thalamic-anterior cingulate pathway.Mol Pain. 2009 Sep 4;5:51. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-51. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19732417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keum S, Shin H-S. Neural basis of observational fear learning: A potential model of affective empathy. Neuron. 2019;104(1):78–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

