Knowledge and management of Münchausen's Syndrome by proxy: a survey conducted through the compilation of a questionnaire by pediatricians belonging to the Italian Society of Pediatrics
- PMID: 40001260
- PMCID: PMC11863681
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-025-01878-z
Knowledge and management of Münchausen's Syndrome by proxy: a survey conducted through the compilation of a questionnaire by pediatricians belonging to the Italian Society of Pediatrics
Abstract
Background: Munchausen syndrome by proxy represent forms of abuse with long-term psychiatric outcomes. Since the prevalence of Munchausen Syndrome by proxy is uncertain and underestimated, this study aimed to investigate and analyze the phenomenon through the compilation of an anonymous questionnaire that explores the knowledge of the phenomenon and above all its management.
Methods: the study was conducted by sending an anonymous questionnaire to pediatricians who are part of the Italian Society of Pediatrics. The questionnaire consists of 18 multiple choice questions and was completed by 511 professionals.
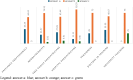
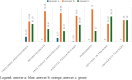
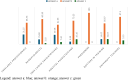
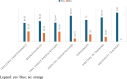
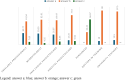
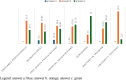
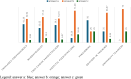
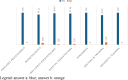
Results: The main results highlighted that the majority of doctors knows Münchausen Syndrome by proxy. However, when there is a strong suspicion of the syndrome, they mostly seek discussion with the parent or with another specialist instead of referring to the competent authorities.
Conclusions: starting from the consideration that timely diagnosis is fundamental for the protection of the child, we emphasize the urgency of enhancing the recognition and management of Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy. Early diagnosis, appropriate reporting, and collaboration with child protection authorities are essential in safeguarding the well-being of vulnerable individuals.
Keywords: Child abuse; Malteatred children; Münchausen Syndrome by proxy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the ethics committee Palermo 1 of “Paolo Giaccone” University Hospital. Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication was obtained. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Furthermore, they declare that the authors Giovanni Corsello and Gregorio Serra have the roles, within Italian Journal of Pediatrics, as Editor in Chief and Associate Editor, respectively.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Medical child abuse, another name for Munchausen's syndrome by proxy].Harefuah. 2009 Aug;148(8):500-1, 574. Harefuah. 2009. PMID: 19899249 Hebrew.
-
Munchausen's syndrome and other factitious disorders.Neurol Clin. 1995 May;13(2):267-81. Neurol Clin. 1995. PMID: 7643825 Review.
-
Munchausen's syndrome by proxy. The question of psychiatric illness in a child.Br J Psychiatry. 1993 May;162:701-3. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.5.701. Br J Psychiatry. 1993. PMID: 8185739 No abstract available.
-
[Munchausen's syndrome by proxy--a malignant form of child abuse].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2000 Nov;9(53):799-802. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2000. PMID: 11204335 Review. Polish.
-
Making children sick. Munchausen's syndrome by proxy.Adv Nurse Pract. 2001 Jun;9(6):103-6. Adv Nurse Pract. 2001. PMID: 12400282 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asher R. Munchausen’s syndrome. Lancet. 1951;6650:339–41. - PubMed
-
- Thomas K. Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy: identification and diagnosis. J Pediatr Nurs. 2003;8(3):174–80. - PubMed
-
- Anderson APA, Feldman MD, Bryce J. Munchausen by Proxy: a qualitative investigation into online perceptions of medical child abuse. J Forensic Sci. 2018;63(3):771–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

