A Genetic and Environmental Analysis of Inflammatory Factors in Chronic Widespread Pain Using the TwinsUK Cohort
- PMID: 40001459
- PMCID: PMC11853120
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15020155
A Genetic and Environmental Analysis of Inflammatory Factors in Chronic Widespread Pain Using the TwinsUK Cohort
Abstract
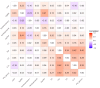
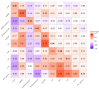
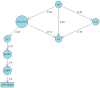
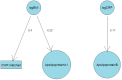
Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain (CWP), a significant health issue affecting individuals and society, is often diagnosed as part of fibromyalgia but is not generally considered inflammatory. This study investigated the relationship between blood-based inflammatory factors and CWP in 904 individuals from the TwinsUK cohort. Participants, free of major inflammatory conditions, completed questionnaires to assess CWP. Plasma samples were analysed using the Olink panel, alongside assays for C-reactive protein (CRP) and Apolipoproteins A1 and B. No significant associations were observed between CWP and inflammatory factors after adjusting for multiple testing. Twin modelling revealed significant heritability for both CWP and inflammatory factors, with genetic covariance observed between CWP and several inflammatory factors. Additive Bayesian network modelling suggested that any association between CWP and inflammatory factors is mediated by body mass index (BMI). These findings emphasize the complexity of CWP and its potential reliance on factors beyond inflammation, such as BMI, which strongly correlates with CRP and other inflammatory markers. Future research should explore additional molecular, genetic, and environmental contributors to CWP variability and investigate clinical factors or covariates that may obscure relationships with inflammation, providing a more comprehensive understanding of this multifaceted condition.
Keywords: CWP; Olink; TwinsUK; chronic widespread pain; fibromyalgia; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nicholl B.I., Macfarlane G.J., Davies K.A., Morriss R., Dickens C., McBeth J. Premorbid psychosocial factors are associated with poor health-related quality of life in subjects with new onset of chronic widespread pain- results from the EPIFUND study. PAIN. 2009;141:119. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.10.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

