Multi-Omics Characterization of Genome-Wide Abnormal DNA Methylation Reveals FGF5 as a Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Recurrence After Radiotherapy
- PMID: 40001587
- PMCID: PMC11853517
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15020283
Multi-Omics Characterization of Genome-Wide Abnormal DNA Methylation Reveals FGF5 as a Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Recurrence After Radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Aberrant expression and mutations in the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family play crucial roles in cell differentiation, growth, and migration, contributing to tumor progression across various cancers. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), a malignancy prevalent in East Asia, is primarily treated with radiotherapy; however, radioresistance remains a major challenge, leading to recurrence and poor outcomes. While FGFs are known to activate signaling pathways such as MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and JAK/STAT to promote cancer progression, the specific role of individual FGFs in NPC radioresistance remains unclear. Emerging evidence highlights FGF5 as a key player in NPC progression, metastasis, and radioresistance, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target to overcome treatment resistance and improve clinical outcomes.
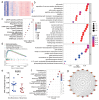
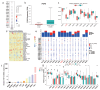
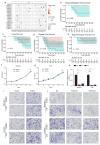
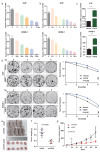
Methods: We analyzed single nucleotide variation (SNV) data, gene expression, and DNA methylation patterns using cancer datasets, including TCGA and GTEx, to investigate FGF5 expression. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified and interpreted using functional enrichment analysis, while survival analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were conducted to identify clinical correlations. DNA methylation patterns were specifically assessed using the HumanMethylation850 BeadChips on tissue samples from nine recurrent and nine non-recurrent NPC patients. Functional assays, including cell viability, migration, invasion, and clonogenic survival assays, were performed to evaluate the effects of FGF5 on NPC cell behavior in vitro and in vivo.
Results: FGF5 showed elevated SNV frequencies across multiple cancers, particularly in HNSC and NPC. DNA methylation analysis revealed an inverse relationship between FGF5 expression and methylation levels in recurrent NPC tumors. Functional assays demonstrated that FGF5 enhances migration, invasion, and radioresistance in NPC cells. High FGF5 expression was associated with reduced distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and increased radioresistance, highlighting its role in metastatic progression and recurrence.
Conclusions: FGF5 plays a significant role in the progression and recurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Its elevated expression correlates with increased migration, invasion, and radioresistance as well as reduced distant metastasis-free survival. These findings suggest that FGF5 contributes to the metastatic and recurrence potential of NPC, making it a potential target for therapeutic intervention in treating these cancers.
Keywords: FGF5; multi-omics characterization; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RPA3 is a potential marker of prognosis and radioresistance for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Nov;21(11):2872-2883. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13200. Epub 2017 May 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28557284 Free PMC article.
-
FOXD1, negatively regulated by miR-186, promotes the proliferation, metastasis and radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Cancer Biomark. 2020;28(4):511-521. doi: 10.3233/CBM-191311. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 32568181
-
DNA methylation biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0230524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230524. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271791 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation Biomarkers for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Prognostic Tools.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(18):8059-65. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.18.8059. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26745039 Review.
-
Research status and prospects of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of high‑throughput omics (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5188. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Environmental Xenobiotics and Epigenetic Modifications: Implications for Human Health and Disease.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jul 13;15(4):118. doi: 10.3390/jox15040118. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40700165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petit C., Lee A., Ma J., Lacas B., Ng W.T., Chan A.T.C., Hong R.L., Chen M.Y., Chen L., Li W.F., et al. Role of chemotherapy in patients with nasopharynx carcinoma treated with radiotherapy (MAC-NPC): An updated individual patient data network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:611–623. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00163-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

