Lipid-siRNA Conjugates Targeting High PD-L1 Expression as Potential Novel Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PMID: 40001596
- PMCID: PMC11852376
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15020293
Lipid-siRNA Conjugates Targeting High PD-L1 Expression as Potential Novel Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Abstract
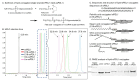
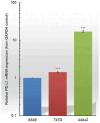
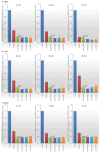
Programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L1), an important immune checkpoint molecule, is mainly expressed on cancer cells and has been shown to exert an immunosuppressive effect on T-cell function by binding to programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) expressed on T-cells. Recently, immune checkpoint inhibitors using antibody drugs such as nivolumab and atezolizumab have attracted attention. However, clinical challenges, including limitations to the scope of their application, are yet to be addressed. In this study, we developed a novel immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets PD-L1 using lipid-siRNA conjugates (lipid-siPDL1s). The inhibitory effect of lipid-siPDL1s on PD-L1 expression was evaluated and found to strongly suppress mRNA expression. Notably, lipid-siPDL1s exerted a significantly stronger effect than unmodified siPDL1. Interestingly, lipid-siPDL1s strongly inhibited PD-L1 expression despite cancer cell stimulation by interferon-gamma, which induced the overexpression of PD-L1 genes. These results strongly suggest that lipid-siPDL1s could be used as novel immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors; interferon gamma (IFNγ) stimulation; nucleic acid drugs; programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L1); siRNA conjugates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Borkner L., Kaiser A., van de Kasteele W., Andreesen R., Mackensen A., Haanen J.B., Schumacher T.N., Blank C. RNA interference targeting programmed death receptor-1 improves immune functions of tumor-specific T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010;59:1173–1183. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0842-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolandi N., Derakhshani A., Hemmat N., Baghbanzadeh A., Asadzadeh Z., Afrashteh Nour M., Brunetti O., Bernardini R., Silvestris N., Baradaran B. The Positive and Negative Immunoregulatory Role of B7 Family: Promising Novel Targets in Gastric Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:10719. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910719. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

