Advances in Huntington's Disease Biomarkers: A 10-Year Bibliometric Analysis and a Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 40001897
- PMCID: PMC11852324
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14020129
Advances in Huntington's Disease Biomarkers: A 10-Year Bibliometric Analysis and a Comprehensive Review
Abstract
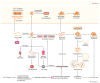
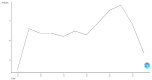
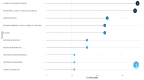
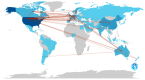
Neurodegenerative disorders (NDs) cause progressive neuronal loss and are a significant public health concern, with NDs projected to become the second leading global cause of death within two decades. Huntington's disease (HD) is a rare, progressive ND caused by an autosomal-dominant mutation in the huntingtin (HTT) gene, leading to severe neuronal loss in the brain and resulting in debilitating motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms. Given the complex pathology of HD, biomarkers are essential for performing early diagnosis, monitoring disease progression, and evaluating treatment efficacy. However, the identification of consistent HD biomarkers is challenging due to the prolonged premanifest HD stage, HD's heterogeneous presentation, and its multiple underlying biological pathways. This study involves a 10-year bibliometric analysis of HD biomarker research, revealing key research trends and gaps. The study also features a comprehensive literature review of emerging HD biomarkers, concluding the need for better stratification of HD patients and well-designed longitudinal studies to validate HD biomarkers. Promising candidate wet HD biomarkers- including neurofilament light chain protein (NfL), microRNAs, the mutant HTT protein, and specific metabolic and inflammatory markers- are discussed, with emphasis on their potential utility in the premanifest HD stage. Additionally, biomarkers reflecting brain structural deficits and motor or behavioral impairments, such as neurophysiological (e.g., motor tapping, speech, EEG, and event-related potentials) and imaging (e.g., MRI, PET, and diffusion tensor imaging) biomarkers, are evaluated. The findings underscore that the discovery and validation of reliable HD biomarkers urgently require improved patient stratification and well-designed longitudinal studies. Reliable biomarkers, particularly in the premanifest HD stage, are crucial for optimizing HD clinical management strategies, enabling personalized treatment approaches, and advancing clinical trials of HD-modifying therapies.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; biomarkers; diffusion tensor imaging (DTI); microRNAs (miRNAs); neurodegenerative disorders; neurofilament light chain (NfL); preHD; premanifest HD; rare diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Sarah Aqel and Jamil Ahmad were employed by the company Hamad Medical Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
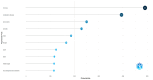

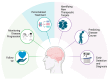
References
-
- Daldin M., Fodale V., Cariulo C., Azzollini L., Verani M., Martufi P., Spiezia M.C., Deguire S.M., Cherubini M., Macdonald D., et al. Polyglutamine expansion affects huntingtin conformation in multiple Huntington’s disease models. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:5070. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05336-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papanna B., Lazzari C., Rabottini M. Huntington’s disease prevalence in Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Riv. Psichiatr. 2024;59:4–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

