Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Inhibits Cell Motility and p-ERK1/2 Signaling in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 40001923
- PMCID: PMC11851717
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14020155
Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Inhibits Cell Motility and p-ERK1/2 Signaling in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
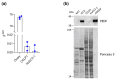
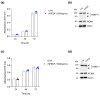
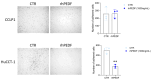
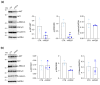
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a multifunctional soluble glycoprotein, primarily known for its potent anti-angiogenic properties. In recent years, its ability to counteract cell proliferation and motility has generated interest in PEDF as a potential tumor suppressor. In the intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), PEDF, Thrombospondin 1 (THBS1), and Thrombospondin 2 (THBS2) are expressed and released into the tumor microenvironment (TME), where they promote lymphangiogenesis at the expense of the neoangiogenic program, aiding the dissemination of cancer cells via lymphatic vessels. Recently, we demonstrated that THBS1 and THBS2 directly affect iCCA cells, exacerbating their malignant behavior, while the direct role of PEDF remains to be elucidated. In this study, through a cell-based assay and molecular analysis, we investigate the direct function of PEDF on two well-established iCCA cell lines. Our results show that PEDF affects cancer cell motility in a paracrine manner, reducing their migratory and invasive capabilities. Notably, our data suggest that the PEDF-induced inhibition of motility in iCCA cells occurs through the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, as indicated by the reduced phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Overall, this study provides the first evidence of PEDF acting as a tumor suppressor in iCCA.
Keywords: PEDF; cell migration; extracellular matrix; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tombran-Tink J., Mazuruk K., Rodriguez I.R., Chung D., Linker T., Englander E., Chader G.J. Organization, evolutionary conservation, expression and unusual Alu density of the human gene for pigment epithelium-derived factor, a unique neurotrophic serpin. Mol. Vis. 1996;2:11. - PubMed
-
- Akiba J., Yoshida T., Sadashima E., Murata K., Matsui T., Yamagishi S.I., Kusano H., Mihara Y., Mizuochi S., Kinjou Y., et al. The Expression of PEDF and its Putative Receptors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Background Liver Tissue. Anticancer. Res. 2021;41:1203–1212. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14877. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

